
[ad_1]
Welcome again! That is the third submit within the reverse engineering sequence. The primary submit was reverse engineering Soundcloud API and the second was reverse engineering Fb API to obtain public movies. On this submit we’ll check out downloading non-public movies. We are going to reverse engineer the API calls made by Fb and can attempt to determine how we will obtain movies within the HD format (when accessible).
Step 1: Recon
The very first step is to open up a non-public video in an incognito tab simply to verify we can’t entry it with out logging it. This needs to be the response from Fb:
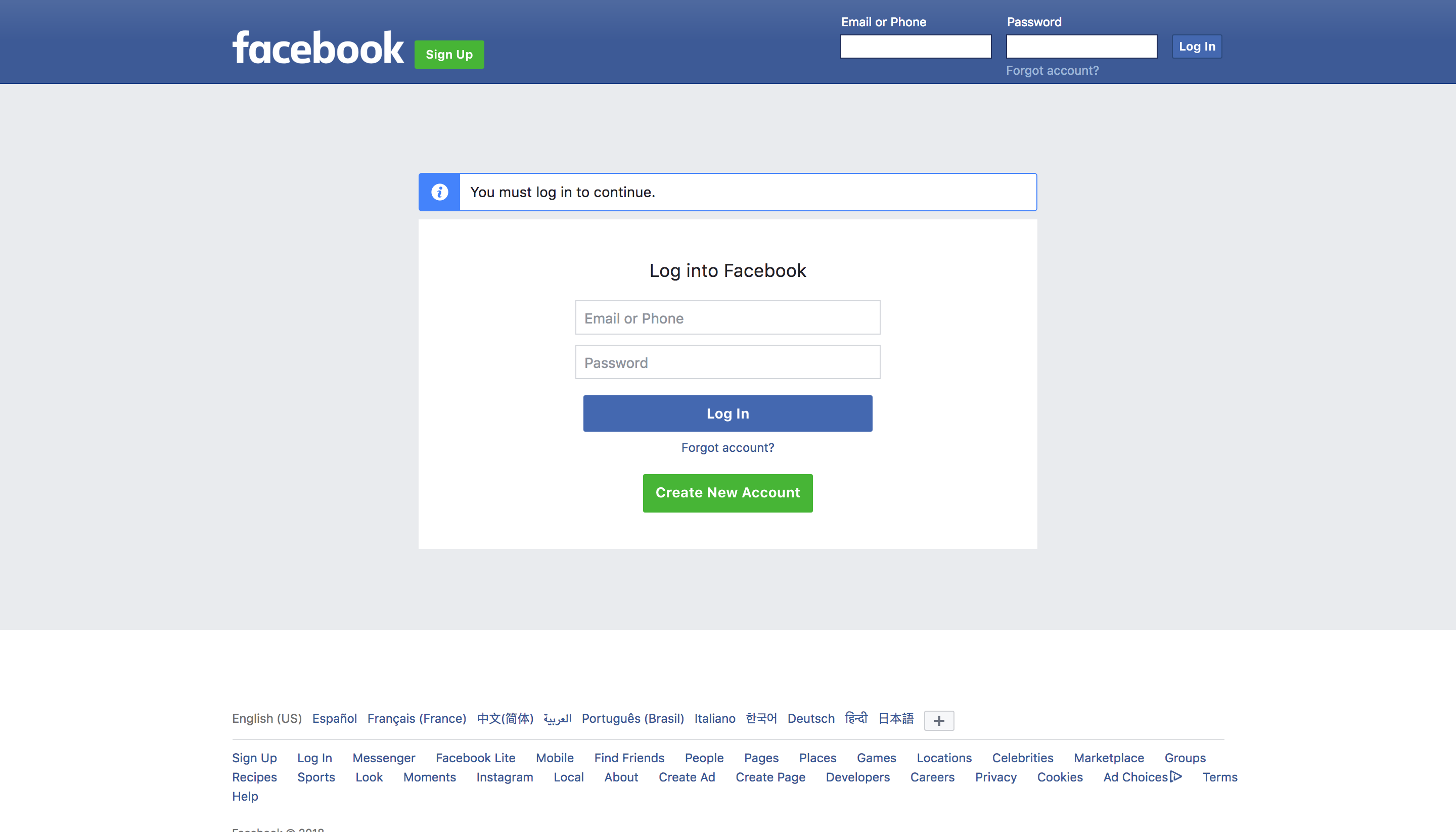
This confirms that we can’t entry the video with out logging in. Typically that is fairly apparent nevertheless it doesn’t damage to test.
We all know of our first step. It’s to determine a solution to log-into Fb utilizing Python. Solely after that may we entry the video. Let’s login utilizing the browser and test what data is required to log-in.
I received’t go into a lot element for this step. The gist is that whereas logging in, the desktop web site and the cellular web site require roughly the identical POST parameters however curiously if you happen to log-in utilizing the cellular web site you don’t have to provide plenty of further data which the desktop web site requires. You may get away with doing a POST request to the next URL together with your username and password:
https://m.fb.com/login.php
We are going to later see that the following API requests would require a fb_dtsg parameter. The worth of this parameter is embedded within the HTML response and might simply be extracted utilizing common expressions or a DOM parsing library.
Let’s proceed exploring the web site and the video API and see what we will discover.
Similar to what we did within the final submit, open up the video, monitor the XHR requests within the Developer Instruments and seek for the MP4 request.
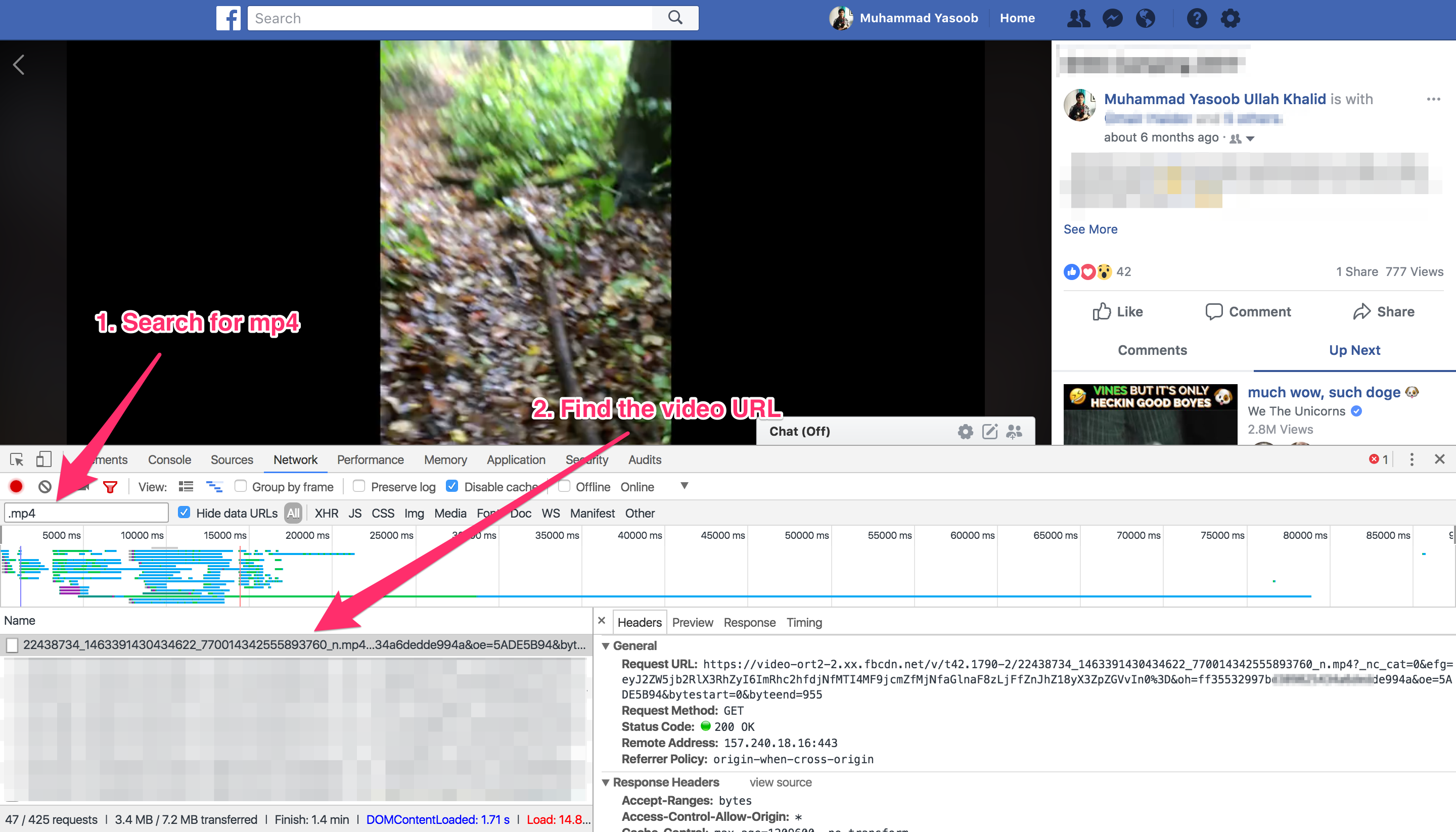
Subsequent step is to determine the place the MP4 hyperlink is coming from. I attempted looking the unique HTML web page however couldn’t discover the hyperlink. Which means Fb is utilizing an XHR API request to get the URL from the server. We have to search by means of the entire XHR API requests and test their responses for the video URL. I did simply that and the response of the third API request contained the MP4 hyperlink:
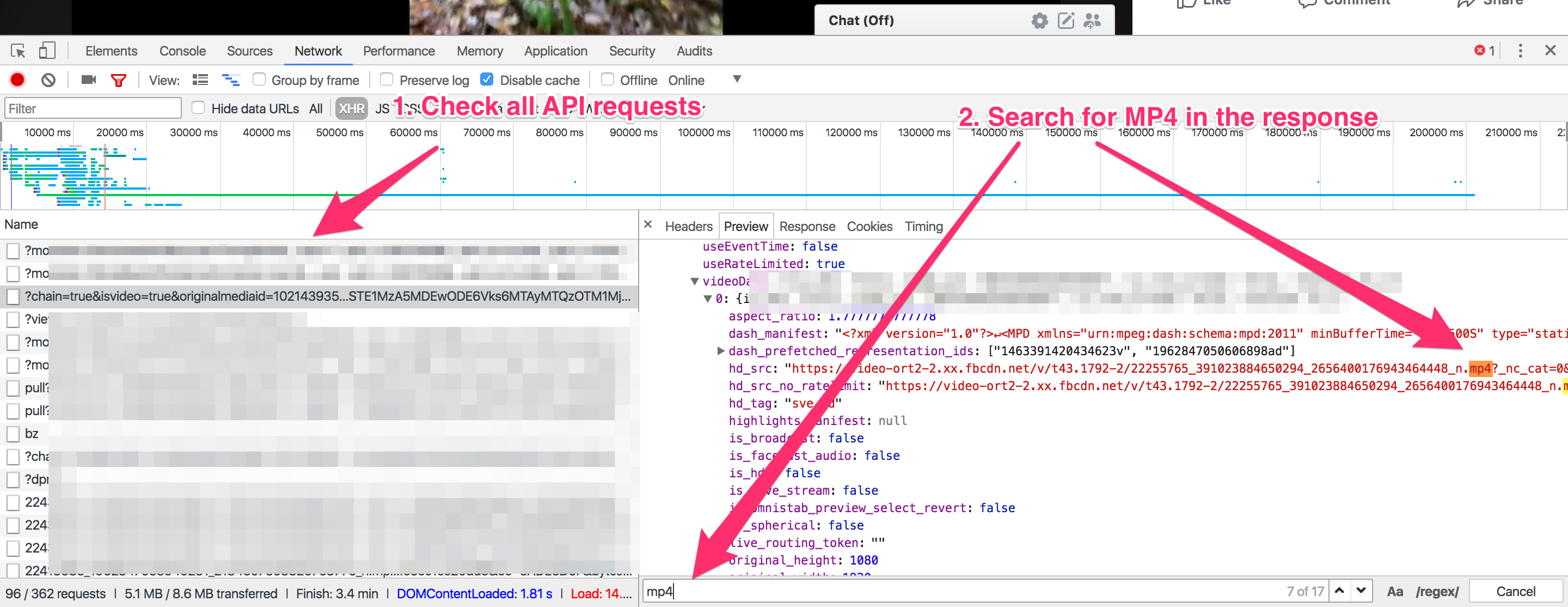
The API request was a POST request and the url was:
https://www.fb.com/video/tahoe/async/10114393524323267/?chain=true&isvideo=true&originalmediaid=10214393524262467&playerorigin=permalink&playersuborigin=tahoe&ispermalink=true&numcopyrightmatchedvideoplayedconsecutively=0&storyidentifier=DzpfSTE1MzA5MDEwODE6Vks6MTAyMTQzOTMNjE4Njc&dpr=2
I attempted to deconstruct the URL. The foremost dynamic elements of the URL appear to be the originalmediaid and _storyidentifier. _I searched the unique HTML web page and located that each of those have been there within the authentic video web page. We additionally want to determine the POST knowledge despatched with this request. These are the parameters which have been despatched:
__user: <---redacted-->
__a: 1
__dyn: <---redacted-->
__req: 3
__be: 1
__pc: PHASED:DEFAULT
__rev: <---redacted-->
fb_dtsg: <---redacted-->
jazoest: <---redacted-->
__spin_r: <---redacted-->
__spin_b: <---redacted-->
__spin_t: <---redacted-->
I’ve redacted many of the stuff in order that my private data is just not leaked. However you get the concept. I once more searched the HTML web page and was capable of finding many of the data within the web page. There was sure data which was not within the HTML web page like _jazoest _but as we transfer alongside you will notice that we don’t really want it to obtain the video. We are able to merely ship an empty string instead.
It looks as if we have now all of the items we have to obtain a video. Right here is an overview:
- Open the Video after logging in
- Seek for the parameters within the HTML response to craft the API url
- Open the API url with the required POST parameters
- Seek for hd_src or sd_src within the response of the API request
Now lets create a script to automate these duties for us.
Step 2: Automate it
The very first step is to determine how the login takes place. Within the recon part I discussed that you could simply log-in utilizing the cellular web site. We are going to do precisely that. We are going to log-in utilizing the cellular web site after which open the homepage utilizing the authenticated cookies in order that we will extract the fb_dtsg parameter from the homepage for subsequent requests.
import requests
import re
import urllib.parse
electronic mail = ""
password = ""
session = requests.session()
session.headers.replace({
'Consumer-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686; rv:39.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/39.0'
})
response = session.get('https://m.fb.com')
response = session.submit('https://m.fb.com/login.php', knowledge={
'electronic mail': electronic mail,
'cross': password
}, allow_redirects=False)
Change the e-mail and password variable together with your electronic mail and password and this script ought to log you in. How do we all know whether or not we have now efficiently logged in? We are able to test for the presence of ‘c_user’ key within the cookies. If it exists then the login has been profitable.
Let’s test that and extract the fb_dtsg from the homepage. Whereas we’re at that allow’s extract the user_id from the cookies as properly as a result of we’ll want it later.
if 'c_user' in response.cookies:
# login was profitable
homepage_resp = session.get('https://m.fb.com/residence.php')
fb_dtsg = re.search('title="fb_dtsg" worth="(.+?)"', homepage_resp.textual content).group(1)
user_id = response.cookies['c_user']
So now we have to open up the video web page, extract the entire required API POST arguments from it and do the POST request.
if 'c_user' in response.cookies:
# login was profitable
homepage_resp = session.get('https://m.fb.com/residence.php')
fb_dtsg = re.search('title="fb_dtsg" worth="(.+?)"', homepage_resp.textual content).group(1)
user_id = response.cookies['c_user']
video_url = "https://www.fb.com/username/movies/101214393524261127/"
video_id = re.search('movies/(.+?)/', video_url).group(1)
video_page = session.get(video_url)
identifier = re.search('ref=tahoe","(.+?)"', video_page.textual content).group(1)
final_url = "https://www.fb.com/video/tahoe/async/{0}/?chain=true&isvideo=true&originalmediaid={0}&playerorigin=permalink&playersuborigin=tahoe&ispermalink=true&numcopyrightmatchedvideoplayedconsecutively=0&storyidentifier={1}&dpr=2".format(video_id,identifier)
knowledge = {'__user': user_id,
'__a': '',
'__dyn': '',
'__req': '',
'__be': '',
'__pc': '',
'__rev': '',
'fb_dtsg': fb_dtsg,
'jazoest': '',
'__spin_r': '',
'__spin_b': '',
'__spin_t': '',
}
api_call = session.submit(final_url, knowledge=knowledge)
attempt:
final_video_url = re.search('hd_src":"(.+?)",', api_call.textual content).group(1)
besides AttributeError:
final_video_url = re.search('sd_src":"(.+?)"', api_call.textual content).group(1)
print(final_video_url)
You may be questioning what the knowledge dictionary is doing and why there are plenty of keys with empty values. Like I mentioned in the course of the recon course of, I attempted making profitable POST requests utilizing the minimal quantity of knowledge. Because it seems Fb solely cares about fb_dtsg and the __person key. You’ll be able to let all the things else be an empty string. Just remember to do ship these keys with the request although. It doesn’t work if the hot button is completely absent.
On the very finish of the script we first seek for the HD supply after which the SD supply of the video. If HD supply is discovered we output that and if not then we output the SD supply.
Our closing script appears one thing like this:
import requests
import re
import urllib.parse
import sys
electronic mail = sys.argv[-2]
password = sys.argv[-1]
print("E mail: "+electronic mail)
print("Cross: "+password)
session = requests.session()
session.headers.replace({
'Consumer-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686; rv:39.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/39.0'
})
response = session.get('https://m.fb.com')
response = session.submit('https://m.fb.com/login.php', knowledge={
'electronic mail': electronic mail,
'cross': password
}, allow_redirects=False)
if 'c_user' in response.cookies:
# login was profitable
homepage_resp = session.get('https://m.fb.com/residence.php')
fb_dtsg = re.search('title="fb_dtsg" worth="(.+?)"', homepage_resp.textual content).group(1)
user_id = response.cookies['c_user']
video_url = sys.argv[-3]
print("Video url: "+video_url)
video_id = re.search('movies/(.+?)/', video_url).group(1)
video_page = session.get(video_url)
identifier = re.search('ref=tahoe","(.+?)"', video_page.textual content).group(1)
final_url = "https://www.fb.com/video/tahoe/async/{0}/?chain=true&isvideo=true&originalmediaid={0}&playerorigin=permalink&playersuborigin=tahoe&ispermalink=true&numcopyrightmatchedvideoplayedconsecutively=0&storyidentifier={1}&dpr=2".format(video_id,identifier)
knowledge = {'__user': user_id,
'__a': '',
'__dyn': '',
'__req': '',
'__be': '',
'__pc': '',
'__rev': '',
'fb_dtsg': fb_dtsg,
'jazoest': '',
'__spin_r': '',
'__spin_b': '',
'__spin_t': '',
}
api_call = session.submit(final_url, knowledge=knowledge)
attempt:
final_video_url = re.search('hd_src":"(.+?)",', api_call.textual content).group(1)
besides AttributeError:
final_video_url = re.search('sd_src":"(.+?)"', api_call.textual content).group(1)
print(final_video_url.substitute('',''))
I made a few adjustments to the script. I used sys.argv to get video_url, electronic mail and password from the command line. You’ll be able to hardcore your username and password if you would like.
Save the above file as facebook_downloader.py and run it like this:
$ python facebook_downloader.py video_url electronic mail password
Change video_url with the precise video url like this https://www.fb.com/username/movies/101214393524261127/ and substitute the e-mail and password together with your precise electronic mail and password.
After working this script, it would output the supply url of the video to the terminal. You’ll be able to open the URL in your browser and from there it’s best to be capable to right-click and obtain the video simply.
I hope you guys loved this fast tutorial on reverse engineering the Fb API for making a video downloader. When you have any questions/feedback/ideas please put them within the feedback beneath or electronic mail me. I’ll have a look at reverse engineering a special web site for my subsequent submit. Observe my weblog to remain up to date!
Thanks! Have an awesome day!
[ad_2]