[ad_1]
Platelet transfusions are important in managing bleeding and hemostatic dysfunction, and will be expanded for use as cell remedy for quite a lot of illnesses. The efforts to create such cell therapies require that researchers modify donor platelets to specific therapeutic proteins. Nonetheless, at current, acceptable strategies to genetically modify platelets collected from blood donors stay elusive.
In a brand new research revealed in Science Advances, Jerry Leung, and a staff of scientists in nanomedicine, biochemistry, and molecular biology on the College of British Columbia, Canada, the Hokkaido College, Japan, and varied establishments within the U.S. described an method primarily based on platelet-optimized lipid nanoparticles containing mRNA for exogenous protein expression in human and rat platelets.
When the staff examined the library of mRNA-lipid nanoparticles, the ensuing exogenous protein expression didn’t correlate with platelet activation. The transfected platelets retained hemostatic perform and accrued in areas of vascular harm after transfusion into rats with the capability to increase the therapeutic potential of the platelets.
Platelets and hemostasis
Platelets are integral to hemostasis and are routinely transfused to revive hemostatic steadiness in sufferers. These platelets will be expanded past indications akin to cell therapies to deal with sepsis, irritation and arthritis. Genetically modified platelets can create new cell therapies that categorical therapeutic proteins, which will be carried out to switch donor platelets. Present strategies of electroporation, viral vectors and business transfection haven’t been in a position to edit donor platelets and categorical exogenous proteins.
Oblique approaches can categorical exogenous proteins in platelets or platelet-like particles by concentrating on platelet precursor stem cells with lentiviral vectors. The donor-derived platelets should be functionally modified to create genuine platelet cell therapies.
Prior makes an attempt to transfect platelets with lipid nanoparticles containing mRNA have proven the potential for mRNA supply into the platelets, whereas advances in lipid nanoparticle expertise have improved its potential to attain a broader demographic.
On this work, Leung and colleagues reported mRNA lipid nanoparticles for his or her capability to straight transfect donor platelets to specific exogenous proteins. Such platelets will be modified with mRNA lipid nanoparticles to take care of their perform and accumulate domestically in wounds and regulate homeostasis after transfusion in coagulopathic rats.
Lipid nanoparticles facilitate exogenous protein expression in platelets
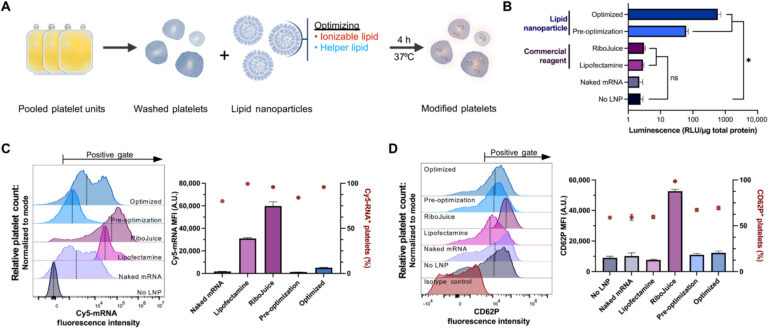
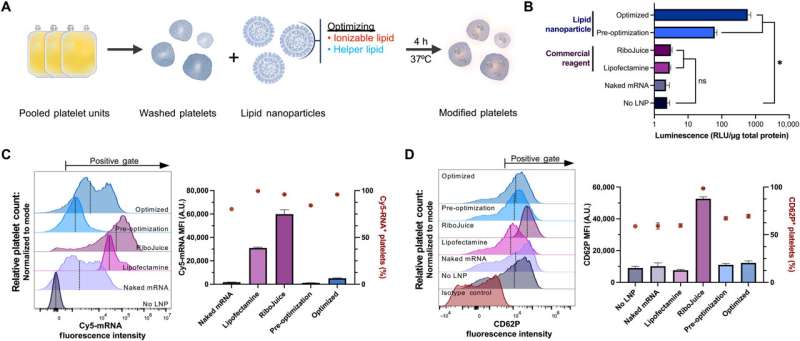
To determine the efficient transfection strategies for platelets, the staff delivered mRNA encoding an enzyme NanoLuc luciferase (NanoLuc) utilizing a number of transfection brokers and measured their expression. Whereas NanoLuc was undetected in platelets handled with free mRNA with out a transfection agent or through the use of business mRNA supply brokers, the method allowed the uptake of enormous quantities of mRNA into the platelets.
Leung and staff detected NanoLuc expression through the use of an mRNA-lipid nanoparticle formulation that resembled the small interfering RNA-lipid nanoparticle clinically confirmed to deal with hereditary amyloidosis. The staff in contrast the quantity of platelet activation following mRNA lipid nanoparticle transfection to untreated platelets.
To determine the mRNA-lipid nanoparticle formulation most suited to move platelets, they optimized three main elements; ionizable lipids, linker lipids, and the polyethylene glycol lipid. They screened 10 ionizable and two completely cationic lipids and measured their protein expression, mRNA uptake and activation to help protein synthesis.
Actions of the functionalized lipid nanoparticles within the lab
To look at how the mix of ionizable and helper lipids have synergistic results to reinforce protein expression whereas minimizing platelet activation, the staff studied two FDA-approved ionizable lipids. Other than their lipid composition, the mRNA parts performed a big position to advertise environment friendly exogenous protein synthesis. The lipid nanoparticles containing helper lipids with a phosphocholine head, alongside lipids with branched or unsaturated tail teams have been most fitted to platelet transfection and to drive larger expression ranges.
Of the RNA modifications examined on this work, Leung and colleagues famous unmodified uridine, or pseudouridine to facilitate larger expression ranges of fluorescence. They then noticed if the expression of fluorescence trusted the diploma of platelet activation, or on the quantity of RNA delivered, which they studied utilizing a correlation matrix evaluation.
Whereas the fluorescence expression didn’t strongly correlate with floor platelet ranges, or mRNA uptake, they famous a light constructive correlation between the quantity of RNA delivered and platelet activation. Since NanoLuc expression didn’t strongly correlate with both floor platelet ranges or mRNA uptake, the staff examined the potential for influencing its expression by activating platelets utilizing agonists earlier than and after mRNA lipid nanoparticle transfection.
Platelet therapy to mannequin dilutional coagulopathy
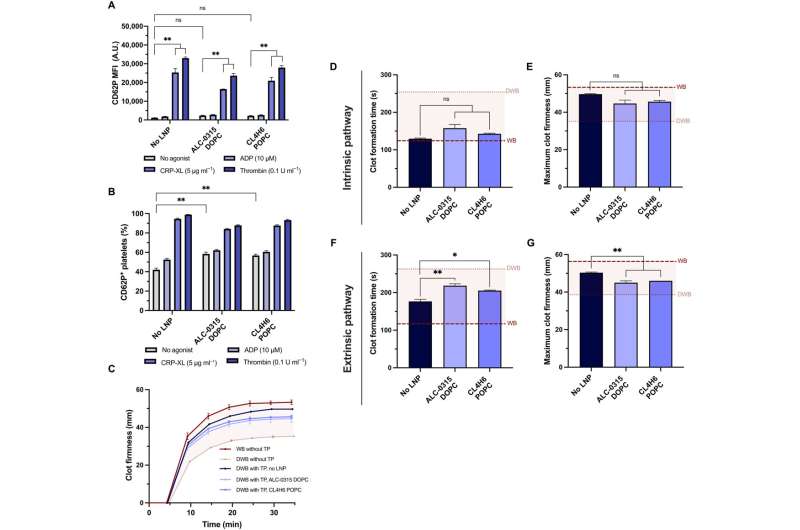
Platelets stimulated with adenosine diphosphate, as an example, cross-linked collagen-related peptide or thrombin previous to the mRNA-lipid nanoparticle therapy, had considerably much less fluorescence expression. When Leung and the staff stimulated platelets with agonists for greater than two hours, they underwent substantial rearrangement of the transcriptome and proteome. The outcomes confirmed that the interpretation of exogenous mRNA didn’t require platelet activation.
When the staff handled platelets with mRNA lipid nanoparticles, they maintained hemostatic perform in vitro and confirmed excessive sensitivity to their bodily and chemical environments. The staff investigated if the platelets might nonetheless be activated after mRNA-lipid nanoparticle transfection and measured their activation state and response to physiological agonists.
The staff examined the capability of transfected platelets to retain their potential to contribute to the firmness and charge of clot formation utilizing a mannequin of rotational thromboelastometry and an ex vivo mannequin to check platelet exercise in entire blood. The researchers modeled dilutional coagulopathy utilizing diluted entire blood and ready platelets in a transfusion package deal.
After they mixed the transfusion package deal with diluted entire blood to mannequin the illness because it happens in a affected person, they famous that the lipid nanoparticles didn’t have an effect on platelet coagulopathy in vitro. Moreover, the staff explored the expression of platelets transfected with mRNA lipid nanoparticles expressed with NanoLuc, circulated and localized into wound websites after transfusion into coagulopathic rodents.
Outlook
On this approach, Jerry Leung and colleagues focused the supply of molecules and cell therapies into vasculature websites of curiosity through the use of the naturally competent platelets that may inherently carry out this job. The staff developed platelet-optimized lipid nanoparticles and mRNA for profitable protein expression, whereas presenting platelet round perform and native accumulation on the vasculature web site of curiosity.
It’s doable to attain the supply of nucleic acids and exogenous translation utilizing platelet-optimized mRNA-lipid nanoparticles to broaden and engineer platelets for quite a lot of scientific purposes. Such donor platelets engineered with mRNA-lipid nanoparticles can deal with acute bleeding issues with broader purposes in oncology. These platelets transfused with optimized mRNA-lipid nanoparticles are functionally transfusable and may accumulate on the vasculature web site for efficient platelet therapies to modulate hematological issues.
Extra info:
Jerry Leung et al, Genetically engineered transfusable platelets utilizing mRNA lipid nanoparticles, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi0508
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Genetically engineered cell therapies with mRNA lipid nanoparticles for transferrable platelets (2023, December 11)
retrieved 16 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-genetically-cell-therapies-mrna-lipid.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]