[ad_1]
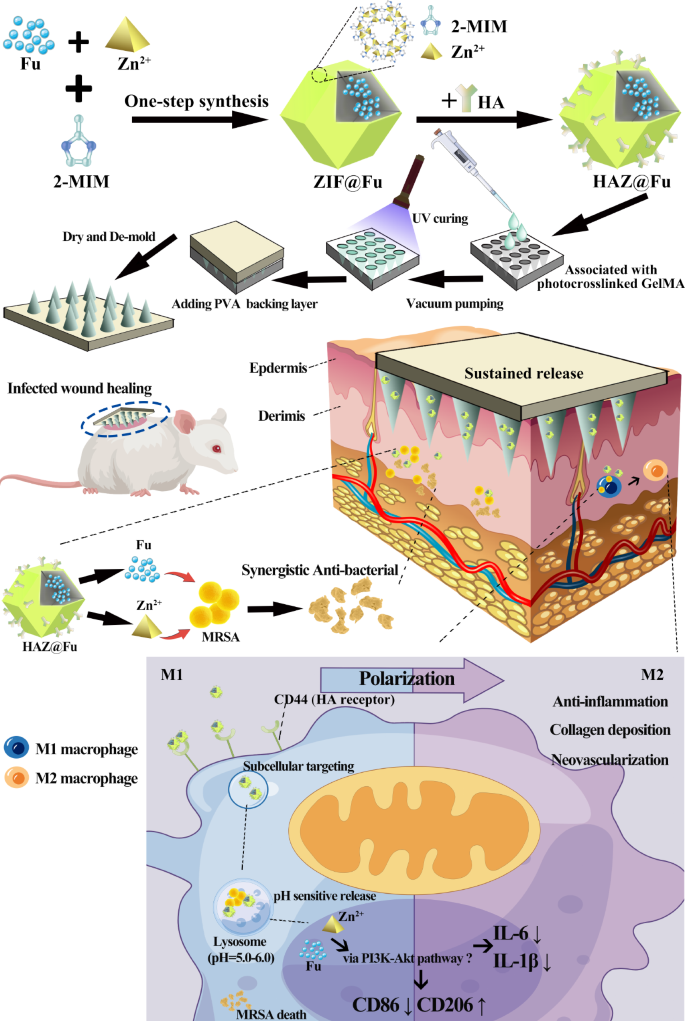
Preparation and characterization of HAZ@Fu
The checklist of abbreviations related to this examine is offered in Desk. S1. Biocompatible and porous ZIF-8 was synthesized by a response between 2-methylimidazole (2-MIM) and Zn2+ salts in DI water. ZIF@Fu was ready utilizing a one-step synthesis technique [27] and the Fu-loading ratio of HAZ@Fu and ZIF@Fu have been detected by an oblique technique [48]. Initially, Fu was combined with Zn2+ salts, permitting the sulfonic acid teams in Fu to type coordination bonds with zinc ions. After additional meeting with 2-MIM, nearly all of Fu molecules have been embedded into the framework, leading to a excessive drug payload. The entire weight of the ZIF, HAZ, ZIF@Fu and HAZ@Fu was measured after freeze-drying. The entire weight of ZIF, HAZ, ZIF@Fu and HAZ@Fu NPs from 20 mL 2-MIM techniques have been 60, 68, 84 and 88 mg, respectively. Then the ZIF@Fu or HAZ@Fu was dissolved destroied by 10 mL EDTA (0.1 M), and the substance apart from Fu was eliminated using a semipermeable membrane with a 1000 Molecular Weight Reduce-Off (MWCO). Then the remaining answer was then lyophilized and weighed to acquire the mass of the encapsulated Fu. The drug-loading effectivity was calculated in keeping with the next method: Drug loading (%) = Wdrug/Wcomplete × 100%. The burden of Fu inside ZIF@Fu or HAZ@Fu was roughly 13.52 mg, and the drug loading effectivity was calculated to be round 16.1%.
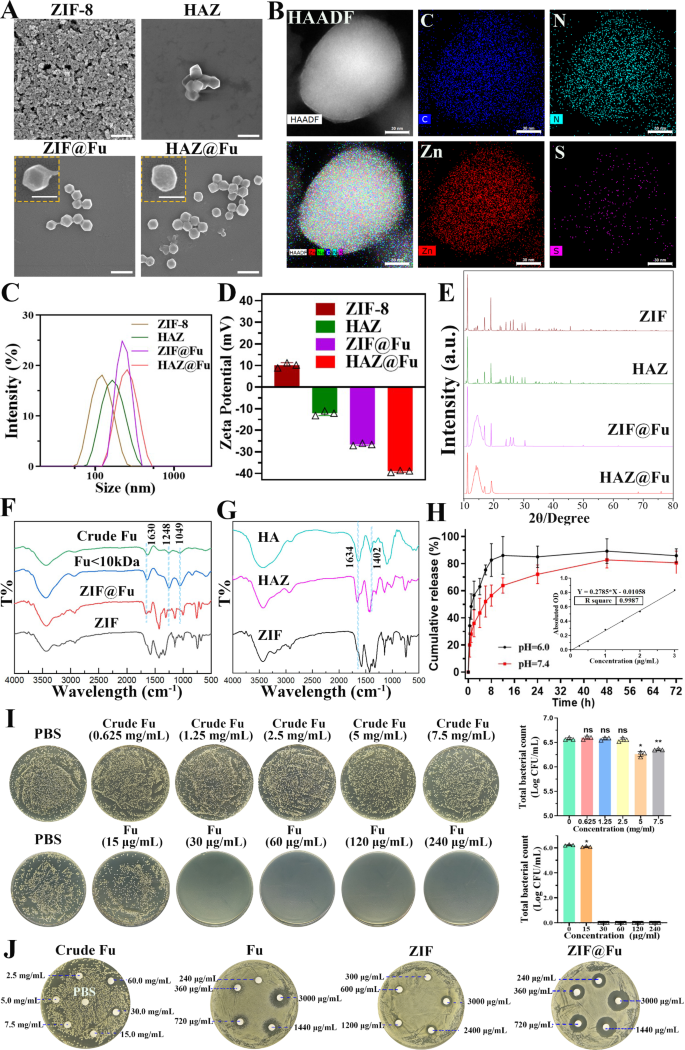
The morphology, particle dimension and floor potential of the NPs have been analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and dynamic gentle scattering (DLS). As depicted in Fig. 1A, each ZIF-8 and ZIF@Fu NPs confirmed a uniform rhombic dodecahedron construction with sharp edges. In distinction, HAZ and HAZ@Fu exhibited smoother edges of the dodecahedron construction, which was possible attributable to the HA coating. DLS revealed that the hydrodynamic diameters of all of the NPs have been bigger in comparison with these noticed within the SEM photos (Fig. 1C; Desk 1). The common hydrodynamic diameter of ZIF-8 was 116.0 ± 0.7 nm. Each Fu loading and HA coating resulted in a rise in diameter, possible because of the extra materials and layers integrated into the nanoparticle construction. Consequently, the diameters of HAZ, ZIF@Fu, and HAZ@Fu NPs measured to be 168.5 ± 1.5, 222.5 ± 3.6, and 283.1 ± 8.4 nm, respectively. The polydispersity index (PDI) of all of the NPs was under 0.3, indicating glorious dispersibility. Initially, ZIF carried a optimistic cost with a zeta potential of 10.10 ± 1.15 mV (Fig. 1D), however transfered to a adverse cost after Fu encapsulation or HA coating, attributable to electronegative teams of Fu. The basic composition of HAZ@Fu NPs was proven in Fig. 1B, decided by factor mappings of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), confirmed the presence of the precise sulfur factor that originated from Fu molecules.
The crystalline construction of NPs was characterised by X-ray diffractometer (XRD). As proven in Fig. 1E, HAZ, ZIF@Fu, and HAZ@Fu exhibited attribute peaks for a crystalline construction just like that of ZIF, with 2θ values of 12.8 and 18.25°. The looks of a novel diffraction peak at 13.8°, coupled with a decreased peak width-to-height ratio within the ZIF@Fu and HAZ@Fu samples, additionally indicated the profitable incorporation of Fu molecules.
Fourier rework infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) evaluation of varied NPs was carried out. As illustrated in Fig. 1F, each the crude Fu and the Fu (Molecular weight < 10 kDa) confirmed attribute peaks at 840, 1049, 1248, and 1630 cm-1, that are attributed to the bending vibrations of C-O-S, stretching vibrations of C-O-C, uneven stretching vibrations of S = O bonds in sulfate moieties, and bending vibrations of O-H teams, respectively. The height depth at 1220–1270 cm-1 was increased for Fu, indicating a better content material of sulfate esters. ZIF@Fu exhibited corresponding peak adjustments at roughly 1049, 1248, and 1630 cm-1 in comparison with ZIF, indicating adequate Fu loading. Related adjustments in FTIR spectra have been additionally noticed within the comparability between ZIF and HAZ (Fig. 1G).
The pH-responsive degradation skill of ZIF-8 NPs was verified utilizing the Zinc Colorimetric Assay Equipment [49], which decided the focus of launched zinc ions. Contemplating the in vivo pH measurements of mouse wounds have revealed that wound pH is mostly barely acidic (pH 5.1) at baseline, and tends to shift in direction of the alkaline vary as scientific an infection progresses [50]. PBS with pH of 6.0 and seven.4 have been particularly chosen to guage the sustained launch of HAZ@Fu. At 8 h, roughly 82.66% of the Zn2+ was launched at pH 6.0, whereas solely 56.49% was launched at pH 7.4 (Fig. 1H). It means that HAZ@Fu NPs retain the pH sensitivity of ZIF-8 and may effectively launch most cargoes in an acidic setting. Moreover, the CCK-8 assay was used to evaluate cell viability of RAW 264.7 cells after 24 h remedy with varied concentrations of Fu or Fu-loaded NPs (Fig. S1). All MOF-based NPs at a focus of 80 µg/mL demonstrated passable biocompatibility.
To additional decide the antibacterial exercise of Fu, ZIF-8, and the Fu-loaded ZIF-8 in vitro, we employed a colony-forming unit (CFU) assay [51] to detect minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBCs). MRSA (> 1 × 106 CFU/mL) have been co-cultured with crude Fu, Fu, ZIF, and ZIF@Fu at totally different concentrations for 16 h. Subsequently, the mixtures have been diluted 100-fold with PBS and inoculated onto Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates, then incubated at 37 °C for twenty-four h. ZIF@Fu towards MRSA was additionally exmined (Fig. S2). Crude Fu exhibited an unreliable antibacterial impact at a focus of seven.5 mg/mL. The MBCs of Fu, ZIF, HAZ, ZIF@Fu, and HAZ@Fu have been round 30, 75, 75, 30, and 30 µg/mL, respectively. As well as, we detected the zones of inhibition (ZOI) of Crude Fu, Fu, ZIF, and ZIF@Fu towards MRSA. As proven in Fig. 1J, crude Fu confirmed no important ZOI at excessive concentrations, whereas the ZOI diameters of Fu, ZIF, and ZIF@Fu (at an equal focus of three mg/mL, which contained 90 µg in filter papers) for MRSA have been 18.10 ± 0.72, 10.60 ± 0.49, and 20.64 ± 1.08 mm, respectively. The ZOI diameter of the ZIF@Fu group was notably bigger than that of the Fu and ZIF group (p < 0.05), aligning with the MBCs take a look at outcomes. Nevertheless, scattered small bacterial colonies nonetheless remained on the edges of the ZOI of the Fu group, whereas no such colonies have been current within the ZIF@Fu group. It demonstrated that each Fu and ZIF possess appreciable antibacterial results, whereas mixture of them may decreased the efficient antibacterial focus, doubtlessly attributable to their mixed skill to wreck the bacterial capsule, thereby considerably affecting bacterial permeability.
Synthesis and characterization of HAZ@Fu MNs
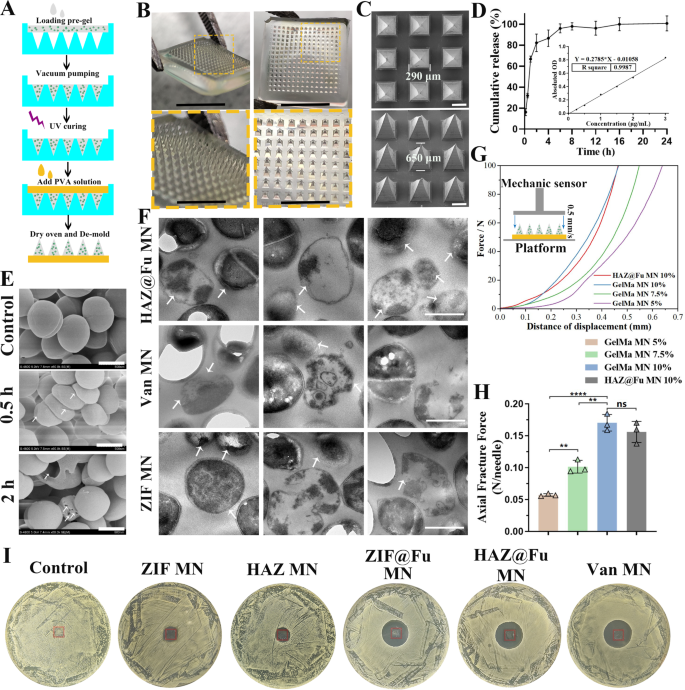
The biocompatible photocrosslinked GelMA hydrogel was chosen as the fabric for MN suggestions, which have been loaded with NPs or Van. Van MNs have been used as a optimistic management for evaluated antibacterial efficacy in vitro or in vivo experiment. PVA was chosen because the backing layer of MNs attributable to its biosafety, mechanical properties, and speedy dissolution. The epidermal layer of human pores and skin is often lower than 250 μm in thickness, additionally contemplating earlier analysis of MNs, we chosen a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) MN mould with a needle size of 650 μm (Fig. S3A), and fabricated the MNs by a two-step template replication technique [40, 41] (Figs. 2 and 3B).
Characterization and antibacterial exercise of free Fu, ZIF NPs and Fu-loaded NPs. (A) SEM photos (scale bar: 500 nm, 200 nm in inset photos). (B) TEM elemental mappings of HAZ@Fu. (C) The scale distribution, (D) zeta potential, and (E) XRD patterns of Zn-MOF derived nanoparticles. (F) FTIR spectra of Fu, crude Fu, ZIF and ZIF@Fu. (G) FTIR spectra of HA, ZIF and HAZ. (H) The discharge curve of Zn2+ derived from the decomposition of ZIF NPs in answer at pH = 7.4 or 5.0 (inset: normal curve of zinc ions). (I) MRSA cells (1 × 106 CFU/mL) resuspended in PBS have been incubated with crude Fu, Fu, ZIF and ZIF@Fu in vitro for 16 h, serially diluted 100-fold with PBS, inoculated onto LB agar plates, then incubated for an additional 24 h. (J) ZOI take a look at of Crude Fu, Fu, ZIF and ZIF@Fu towards MRSA
Fabrication and characterization of the HAZ@Fu MNs. (A) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of a HAZ@Fu MN patch. (B) Isometric and tip-upward photographic photos of a HAZ@Fu MN patch, together with the corresponding zoomed-in photos (scale bar: 5 mm and a couple of mm, respectively). (C) SEM photos of the HAZ@Fu MN patch. (D) Cumulative launch of Zn2+ from the HAZ@Fu MN patch. (E) SEM photos of MRSA co-cultured with HAZ@Fu MN in PBS, arrows point out distorted and disintegrated MRSA (scale bar: 500 nm). (F) TEM photos of MRSA co-cultured with HAZ@Fu MN, Van MN and ZIF MN in PBS for twenty-four h, arrows point out distorted and disintegrated MRSA (scale bar: 500 nm). (G) Power‒displacement curves of MNs with totally different compositions (inset: schematic diagram of the mechanical power take a look at). (H) The axial fracture forces of the totally different MNs. (I) ZOI take a look at of various MNs towards MRSA, crimson rectangle indicated the place of MNs
The Fig. 3B presents a photographic picture of the MN patch, which consists of a 15 × 15 array of microneedles. The SEM photos confirm that the MN suggestions are pyramidal in form and are neatly arrayed on the backing layer, as proven in Fig. 3C, the size of the MN suggestions embody a base size of 290 μm and a peak of 650 μm. This sharp pyramidal construction allowed for fast, noninvasive pores and skin insertion, as additional examined in mouse pores and skin. As proven in Fig. S3B-D, the MN was inserted into the mouse pores and skin. The traces of puncture channels, stained with methylene blue, have been visibly current on the pores and skin tissue. Histological evaluation utilizing frozen sections stained with H&E additionally offered in Determine S4, the marked arrows point out channels produced by the MN insertion breached the stratum corneum barrier and prolonged into the dermal layer. The chanal spacing corresponds exactly to the form of the microneedle suggestions, with penetration exceeding 300 μm into the subcutaneous layer. This confirmed that the MNs possess sufficient mechanical power to penetrate the dermis of the pores and skin successfully. The HAZ@Fu MNs was then co-cultured with MRSA in 1 mL of PBS. SEM was employed to watch the morphological adjustments in MRSA at varied time factors. Important distortions in MRSA have been noticed inside 0.5 h, and bacterial capsules began disintegrate by 2 h (Fig. 3E). TEM was additionally employed to watch the MRSA after incubated with HAZ@Fu MN, Van MN and ZIF MN for twenty-four h. As proven in Fig. 3F, it clearly reveals that in all three teams, there may be evident destruction of the MRSA capsule construction and lysis of the bacterial cells (indicated by arrows). Each SEM and TEM verified the superb in vitro antibacterial exercise of HAZ@Fu MN.
To look at the discharge kinetics of the HAZ@Fu MN, the MNs have been immersed in 1 mL PBS, the focus of zinc ions within the launched system was measured over time. The discharge profile demonstrated a sustained launch sample, with a cumulative launch price of 82.27 ± 8.36% detected at 2 h (Fig. 3D). LB agar plates have been employed to simulate the localized temperature pores and skin wound tissue by inserting them in a 37 °C incubator. Following the applying of the MN into the LB agar plates, we noticed the degradation of the MNs over varied time intervals. When the MN patch was inserted into an LB agar plate at 37 °C, it nearly fully dissolved inside 2 h (Fig. S5), aligning completely with the discharge profile of the HAZ@Fu MN. Moreover, solely 40-50% of zinc ions have been launched from the ZIF@Fu NPs on the 2h (Fig. 1H), indicating that the NPs possess a extra sustained launch impact in comparison with MNs. The mixture of MNs with NPs is prone to create a longer-acting, extra dependable managed launch system, whereas the MN construction additional ensures an prolonged period of motion for the NPs.
We evaluated the mechanical properties of the MNs utilizing an digital stress testing machine to check the utmost pressure capability of their needle suggestions. The MNs have been first positioned on a horizontally positioned mounted station with suggestions going through a pressure sensor that slowly approached the MNs. The pressure measurements started when the sensor touched the MN suggestions and continued till the measured worth reached 100 N. The pressure‒displacement curve of every pattern was recorded (Fig. 3G), with the Younger’s modulus and the Axial Fracture Power obtained when the sensor traveled 0.3 mm, serving because the stiffness index of the MNs (Fig. S7A and Fig. 3H). The Younger’s modulus of MNs was elevated with the rise of GelMA focus, indicating the enhancement of the mechanical power of the MNs (p < 0.05). A rise within the GelMA focus led to a rise within the Younger’s modulus of the MNs, indicating an enhancement of their mechanical power (p < 0.05). At a GelMA focus of 10%, the MNs may face up to compressive forces of 0.17 ± 0.013 N/needle, sturdy sufficient to efficiently puncture the pores and skin [52]. The loading of NPs didn’t considerably alter their mechanical power (p > 0.05). To guage the antibacterial exercise of the drug-loaded MNs, the ZIF MNs, HAZ MNs, ZIF@Fu MNs, HAZ@Fu MNs, and Van MNs have been incubated with MRSA at 37 °C for twenty-four h. As noticed in Fig. 3I and Fig. S7B, ZOI in MRSA have been brought on by ZIF@Fu MN, HAZ@Fu MN, and Van MN, with diameters of twenty-two.27 ± 0.40, 23.56 ± 0.67, and 25.02 ± 0.59 mm, respectively. In distinction, each ZIF MN and HAZ MNs have been solely in a position to inhibit bacterial progress throughout the patch protection space, and their ZOI diameters have been considerably smaller than these of the ZIF@Fu MN, HAZ@Fu MN, and Van MN teams (p < 0.05). Naked MNs didn’t exhibit any antibacterial impact. Consequently, the antibacterial efficiency of the HAZ@Fu MNs was strong, approaching that of the Van MNs.
Mobile uptake effectivity of NPs
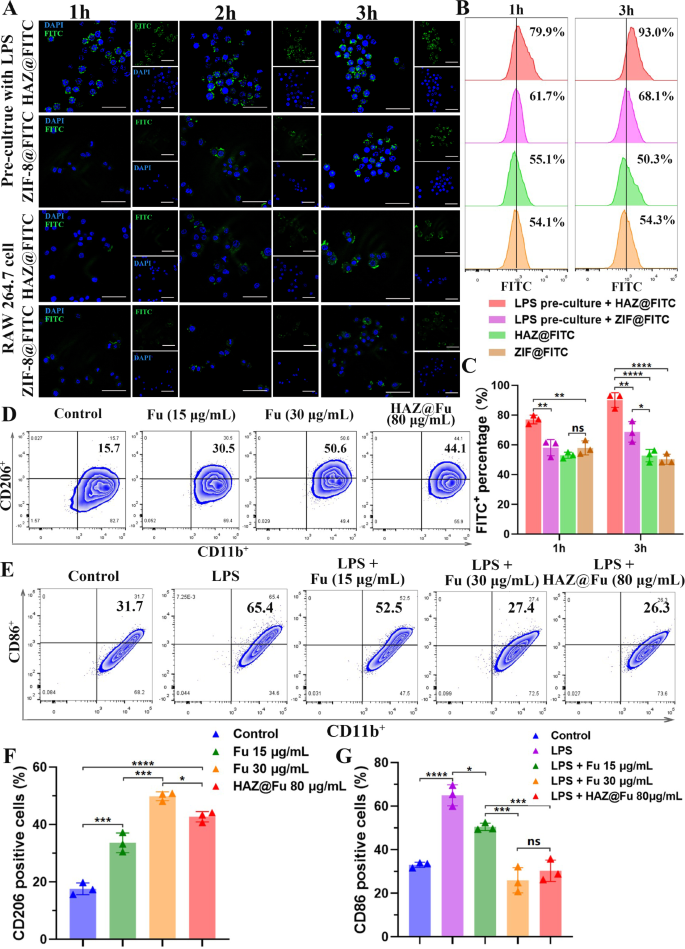
To guage the uptake effectivity of HAZ@FITC NP in each the M1-polarized RAW cells and the M0 RAW cells, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to activate macrophages into the M1 phenotype. The charges of M1 polarization (indicated by CD86+) have been examined by move cytometry (FCM). As illustrated in Fig. S8, the degrees of the primary M1 marker, CD86, considerably elevated after treating RAW 264.7 cells with LPS (100 ng/mL) for twenty-four h, growing from 22.6 to 65.8%. As proven in Fig. 4A, solely the M1 polarized RAW cells + HAZ@FITC group displayed noticeable FITC alerts at 1 h. The FITC fluorescence sign was predominantly localized across the DAPI-stained nuclei, indicating speedy internalization of the nanoparticles into the cytoplasm of the cells. Amongst all of the teams, the M1 polarized RAW cells within the HAZ@FITC group exhibited the very best FITC fluorescence sign depth. Furthermore, the fluorescence depth of all teams elevated from 1 to three h, suggesting the impact was time-dependent.
(A) Confocal microscopy photos of FITC-loaded NPs uptake by untreated RAW cells or RAW cells precultured with LPS for 1, 2 and three h (scale bar: 50 μm). (B) The FCM outcomes of the FITC sign to show the uptake effectivity of NPs at 1 and three h, stained with FITC and F4/80. (C) The FITC-positive share of cells cultured with FITC-loaded NPs after 1 and three h. (D) The FCM outcomes of BMMs cultured with regular medium and medium cotaining Fu (15 and 30 µg/mL, repectively) or HAZ@Fu NPs (80 µg/mL) for twenty-four h, stained with the M2 marker CD206, and macrophage markers CD11b (gated by F4/80). (E) FCM outcomes of BMMs cultured with regular medium and medium containing LPS (100 ng/mL), LPS + Fu or LPS + HAZ@Fu NPs stained with the M1 marker CD86 and macrophage marker CD11b (gated by F4/80). (F) Ratio of BMMs stained with M2 marker CD206. (G) Ratio of M1 phenotype BMMs stained with M1 marker CD86
The uptake effectivity was additional quantified utilizing FCM (Fig. 4B, C). The M1 polarized RAW cells + HAZ@FITC group additionally demonstrated the very best FITC fluorescence depth (77.10 ± 2.91% at 1 h and 90.20 ± 4.94% at 3 h). In distinction, the M1 polarized RAW cells + ZIF@FITC group solely achieved 58.23 ± 5.49% at 1 h and 68.8 ± 6.88% at 3 h. These outcomes counsel that an upregulation of CD44 expression in M1 polarized cells permits for the elevated uptake of HA-coated nanoparticles.
Results of Fu and HAZ@Fu NPs on the polarization of macrophages
The polarization of Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) was additionally investigated by detecting the M1 marker CD86 and the M2 marker CD206 utilizing FCM. Determine 4D and F reveal that after 24 h of co-culture, the M2 phenotype of BMMs was activated by Fu and Fu-containing NPs. The odds of CD206 optimistic cells after cultured with Fu at concentrations of 15 µg/mL (33.67 ± 3.42%), 30 µg/mL (49.87 ± 1.54%) and with 80 µg/mL HAZ@Fu NPs (42.73 ± 1.80%), which have been notably increased than that of management group (17.63 ± 2.06%, p < 0.05). Moreover, Fu or HAZ@Fu NPs may inhibit the M1 polarization of BMMs induced by LPS. As displayed in Fig. 4E and G, the proportion of CD86 optimistic cells after cultured with LPS (100 ng/mL for twenty-four h) was 65.00 ± 4.81%, whereas within the LPS + 15 µg/mL Fu group was 50.53 ± 1.71%, within the LPS + 30 µg/mL HAZ@Fu NPs group was 25.97 ± 5.77% and within the LPS + 80 µg/mL HAZ@Fu NPs group was 30.33 ± 4.91%. The FCM take a look at was additionally carried out after BMMs co-cultured with HAZ@Fu NPs (40 and 80 µg/mL) for 48 h, as proven in Fig. S9, The presence of CD206 optimistic cells was 16.6% within the management group. After coculture with the HAZ@Fu for 48 h, there was additionally a marked improve within the inhabitants of CD206 optimistic cells. Within the group handled with 40 µg/mL of HAZ@Fu, the proportion of CD206 optimistic cells rose to 26.2%, and within the group handled with 80 µg/mL of HAZ@Fu, it elevated considerably to 51.5%.
Each Fu and Fu-loaded NPs facilitate M2 polarization and inhibit M1 polarization of macrophages in a dose- and time-dependent method. Remarkably, 80 µg/mL HAZ@Fu NPs with approximate 10.48 µg/mL Fu match the M1 inhibitory impact of 30 µg/mL free Fu, possible attributable to enhanced HA-coated NP uptake by M1 macrophages or intrinsic exercise of HA.
Gene expression profle of BMMs analyzed by microarray
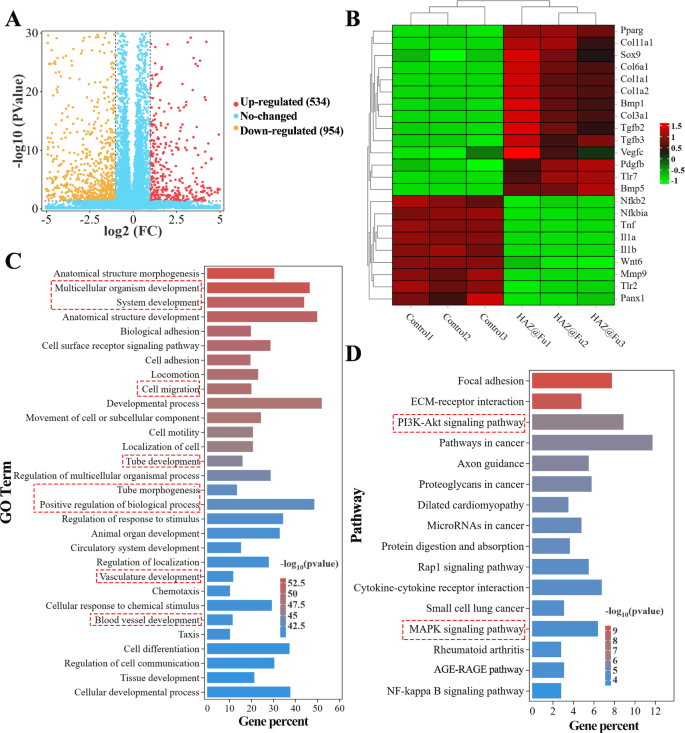
RNA sequencing was employed to detect the entire mRNA expression of BMMs cultured with or with out HAZ@Fu NPs for twenty-four h. As proven in Figs. 5A and 1488 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the HAZ@Fu and management group have been recognized, with 534 genes upregulated and 954 genes downregulated in HAZ@Fu cluster (greater than 2-fold adjustments in expression). From these genes, we recognized these associated to irritation (similar to IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF, MMP, and NFκB) and tissue restore (together with Pparg, Col1a, VEGF-c, and TGF-β) as related to our examine. We then created warmth maps to visually signify the expression ranges of those chosen elements (Fig. 5B). The outcomes revealed that within the HAZ@Fu group, anti-inflammatory elements, anti-inflammatory pathway proteins, and tissue repair-related elements have been extremely expressed, whereas inflammatory elements or inflammatory pathway proteins have been expressed at decrease ranges. As demonstrated in Fig. S10A, the Gene Ontology (GO) perform enrichment evaluation indicated that DEGs have been primarily enriched in organic processes (BP). Subsequently, a particular GO perform enrichment of BP was carried out, with the highest 30 most enriched GO phrases within the HAZ@Fu group in contrast with the management group, indicating that DEGs have been enriched developmental process-related BP, together with cell migration, tube morphogenesis and tube/vasculature/blood vessel improvement (Fig. 5C). The reactome enrichment evaluation revealed DEGs predominantly enriched in extracelluar matrix group and collagen formation (Fig. S10B). CD 206 optimistic cells.
RNA sequencing was employed to detect the entire mRNA expression of BMMs cultured with HAZ@Fu NPs or regular tradition medium for twenty-four h. (A) Volcano plot exhibiting the Gene expression variations between the HAZ@Fu and Management group. (B) Microarray warmth map depicting the fold change of chosen genes expression. (C) The 30 foremost GO phrases within the HAZ@Fu group in contrast with these within the management group, with the very best enrichment ranges have been chosen based mostly on the p-value. (D) Consultant 16 associated pathways analyzed by KEGG pathway enrichment technique
To additional perceive the signaling path methods concerned in regulating macrophage phenotype switching and tissue regeneration gene expression, kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway evaluation was utilized. Determine 5D revealed the primary 16 associated pathways enriched between HAZ@Fu and management group. Particularly, the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is related to the M1 phenotype, confirmed a slight downregulation, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, a key pathway regulating M2 polarization, anti-inflammatory responses, and angiogenesis [53, 54], was signifcantly enriched by KEGG evaluation. Briefly, the RNA sequencing information advised that HAZ@Fu can instigate a change within the gene expression profile of macrophages in direction of the M2 phenotype, selling collagen deposition, tissue regeneration, and angiogenesis. The KEGG evaluation signifies these capabilities are possible completed by means of the PI3K-Akt pathway, though additional validation is actually required.
Intracellular destiny and intracellular exercise of ZIF and HAZ NPs
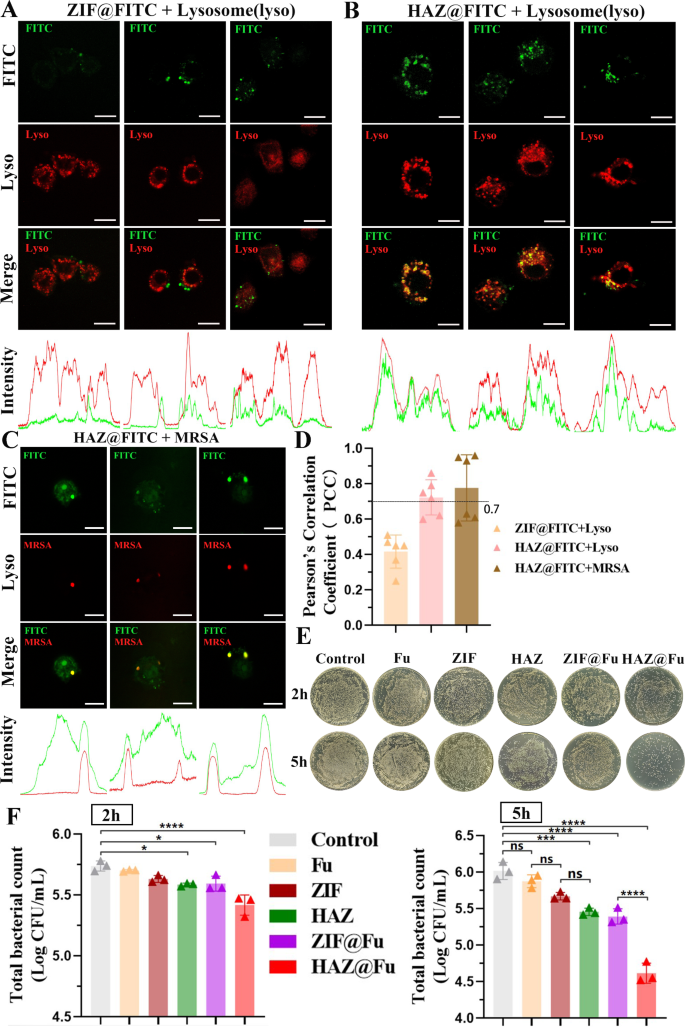
To discover the potential colocalization of HAZ NP with lysosomes, provided that the uptake of NPs in RAW 264.7 cells was noticed to rise progressively over the preliminary 3 h, RAW 264.7 cells have been incubated with both ZIF@FITC or HAZ@FITC NPs for 4 h, after that, the cells stained with Lyso-tracker Crimson DND-99. Stay cell photos have been then recorded utilizing confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). As well as, the Plot Profile characteristic of ImageJ software program was utilized to explain the distribution of the fluorescence sign. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) is the metric usually used to quantify the diploma of colocalization between totally different fluorescence alerts. The PCC between totally different fluorescence alerts was decided based mostly on a complete of 6 photos derived from three impartial experiments.
As illustrated in Fig. 6A and B, a major correlation was noticed between the HAZ@FITC sign and lysosomes, the depth photos confirmed a excessive concurrence between the peaks of the crimson and inexperienced fluorescence alerts. Conversely, the ZIF@FITC group didn’t show a major correlation with lysosomal fluorescence, yielding a PCC worth of 0.42 ± 0.09. These findings affirm that HAZ NPs are able to accumulating within the lysosomes of RAW 264.7 cells.
(A) Colocalization of ZIF@FITC NPs with lysosomes. RAW 264.7 cells have been incubated with 60 µg/mL FITC-loaded NPs for 4 h. Then the slides have been rinsed with PBS and handled with LysoTracker Crimson for five min at 37 °C. Pictures have been instantly captured from stay cell (scale bar: 10 μm). (B) Colocalization of ZIF@FITC NPs with lysosomes (scale bar: 10 μm). (C) Colocalization of HAZ NPs with intracellular MRSA. RAW 264.7 cells have been incubated with MRSA (marked by mCherry). After which extracellular micro organism have been eliminated, the cells have been then rinsed with PBS and additional incubated with 80 µg/mL HAZ@FITC NPs for 3 h. Pictures have been captured utilizing CLSM (scale bar: 10 μm). (D) PCC was calculated utilizing ImageJ. (E) Contaminated RAW 264.7 cells have been incubated with Fu, ZIF, HAZ, ZIF@Fu, HAZ@Fu, and PBS for two and 5 h. Subsequently, all cells have been lysed, and 100 µL of every lysate (10-fold dilution) was cultured on LB agar plates and incubated for twenty-four h. Digital photos of the plates have been captured. (F) Viable cell counts have been calculated utilizing three organic replicate rely information (every derived from three technical replicate information). All information proven are viable counts multiplied by 100 (dilution a number of), with log10 reworked
To additional discover the potential of HAZ NPs to focus on intracellular MRSA at a subcellular stage, the MRSA (USA 300) have been labeled with inexperienced fluorescent protein (GFP) or mCherry for the fluorescent monitoring. RAW 264.7 cells an infection mannequin was established by coculturing with MRSA for 1 h, and utilizing FBS-free DMEM containing Van at a concentretion of two×MIC to take away any extracellular micro organism. The contaminated cells have been cocultured with HAZ@FITC for 3 h and washed twice with PBS, then noticed by CLSM instantly (Fig. 6C and Fig. S11A). It additionally discover a important correlation between the FITC sign and MRSA, indicated by the PCC values above 0.7 for each lysosomes (0.72 ± 0.10) and MRSA (0.77 ± 0.19) when colocalized with FITC-labeled HAZ nanoparticles. Moreover, the colocalization of MRSA (labelled with GFP) with lysosomes was additionally detected by CLSM (Fig. S11B), it demonstrated that just about all of the internalized micro organism have been discovered within the lysosomes throughout the cells (indicated with arrows). This amassed proof strongly suggests the excessive effectivity of HAZ NPs in focusing on intracellular MRSA in macrophages.
To guage the intracellular exercise of HAZ@Fu NPs, RAW 264.7 cells an infection mannequin have been handled with Fu, ZIF NPs, HAZ NPs, ZIF@Fu NPs, and HAZ@Fu NPs (all teams at an equal focus of 60 µg/mL) for two or 5 h. Subsequently, cells have been lysed utilizing 0.025% Triton X, and lysates have been collected and serially diluted with sterile PBS, then inoculated onto LB agar plates, and incubated for twenty-four h. As proven in Fig. 6E and F, after 2 h of incubation, HAZ@Fu exhibited essentially the most important antimicrobial exercise (p < 0.05). After 5 h of incubation, each ZIF@Fu and HAZ@Fu displayed important antimicrobial exercise towards intracellular MRSA. Whereas the pure Fu confirmed a restricted impact on intracellular MRSA, each ZIF and HAZ confirmed increased efficacy in comparison with the management group (p < 0.05). The excessive effectivity of HAZ@Fu in treating intracellular MRSA might be attributed to: I) The optimum dimension of NPs facilitating cell uptake, II) The antibacterial results of each Fu and ZIF, with their mixture within the drug-loading system producing a synergistic impact and thereby lowering the efficient antibacterial focus, and III) The HA coating offering particular intracellular bacterial focusing on.
Analysis of therapeutic in MRSA-infected wounds in vivo
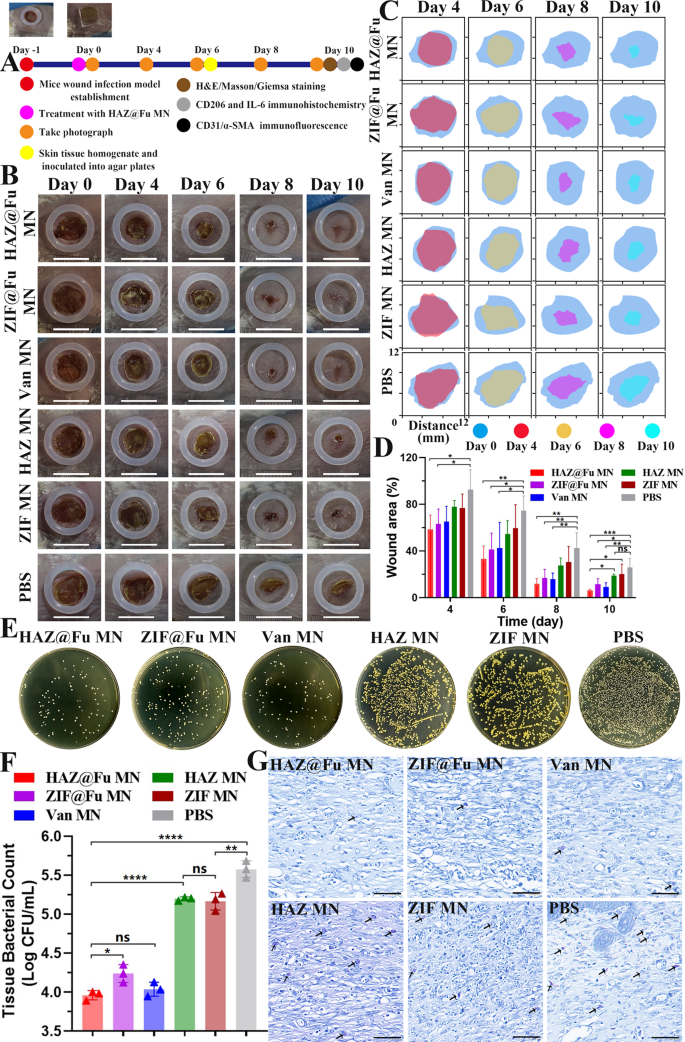
In vivo experiments have been carried out in feminine BALB/c mice between 6 and eight weeks. To determine a full-thickness contaminated cutaneous defect mouse mannequin, a spherical wound with 0.8 cm have been created on the again of mice, and 50 µL PBS containing MRSA have been subsequently inoculated. The mice have been randomly divided into 6 teams. The group with none remedy served because the management. The opposite 5 teams have been handled with ZIF MN, HAZ MN, ZIF@Fu MN, HAZ@Fu MNs, and Van MN (pure Van loaded into MNs), respectively. MNs have been utilized on to the injuries with acceptable stress to allow the microneedles to penetrate the pores and skin, and the dissolution course of was additionally noticed. As proven in Fig. S6, 15 min after the remedy, the contact floor turned moist, indicating that the GelMA hydrogel needles had began to dissolve noticeably. Subsequently, at 60 min, the backing layer turned visibly damp and commenced to degrade. At 150 min solely the residual shapes of the microneedle bases have been left, and by 300 min, a gel-like substance remained on the floor of the wound, making a protecting layer. In comparison with the dissolution on LB plates, the PVA within the backing layer dissolved extra slowly, That is possible attributed to the decrease temperature of the backing layer, ensuing from the shortage of direct contact with the pores and skin, versus the secure temperature and humidity situations current on the LB plates. Nonetheless, the realm of pores and skin contact with the microneedles additionally turned quickly moist, indicating that the microneedles dissolved rapidly. Your complete experimental process is illustrated in Fig. 7A.
Remedy effectivity of the MNs on MRSA-infected wounds. (A) Illustration of the experimental procedures for in vivo remedy of contaminated wounds. (B) Consultant images of wounds with varied therapies at totally different time factors. As a reference, a rubber ring with an interior diameter of 1 cm was positioned across the wound (scale bar: 10 mm). (C) Simulation of wound morphological transformations over a span of 10 days. (D) Comparative evaluation of the relative wound space amongst totally different teams over 10 days. (E) Consultant images and (F) Corresponding histograms of bacterial colonies derived from MRSA-infected tissue homogenates after present process numerous therapies on Day 6. G) Giemsa staining of wound tissues post-10 days remedy (scale bar: 50 μm). Micro organism are indicated by arrows
Dynamic adjustments in wound morphology in Fig. 7B and C revealed that the wound in each the HAZ@Fu MNs and Van MNs teams have been practically full therapeutic after 10 days. Whereas the injuries within the ZIF MNs, HAZ MNs, and management teams exhibited a slower therapeutic course of, with seen scabs remaining. Measurements and evaluation of the wound closure price for every group have been carried out utilizing digital imaging methods (Fig. 7C and D). On day 4, the relative wound areas within the HAZ@Fu MNs and ZIF@Fu MNs teams have been 58.60 ± 12.18% and 63.11 ± 12.91%, respectively, and additional diminished to 12.08 ± 4.38% and 16.9 ± 7.32% on day 8, representing a considerably higher therapeutic price than that of the management group (42.74 ± 12.95%). The epidermal scabs of the HAZ@Fu MNs, ZIF@Fu MNs, and Van MNs teams have been fully shed, indicated a accomplished epithelial tissue regeneration course of. HAZ@Fu MNs teams achieved a wound closure price exceeding 90%, considerably increased than each the HAZ MNs and the management group (p < 0.05). It demonstrated that HAZ@Fu possesses efficient antibacterial exercise and likewise promotes tissue regeneration in wounds.
The in vivo antibacterial effectivity was additionally evaluated. On day 6, pores and skin tissue containing the whole wound space have been collected from all teams for tissue homogenization. The homogenate was subsequently serially diluted with PBS and inoculated onto LB agar plate, incubated for twenty-four h and the viable cell counts have been decided. As illustrated in Fig. 7E, a noticeable lower within the variety of colony-forming items was noticed after remedy with HAZ@Fu MNs and Van MNs, and no substantial distinction was famous between them (p > 0.05). Nevertheless, ZIF@Fu MNs group displayed a decrease bacterial killing effectivity than Van MNs group in vivo (p < 0.05). As proven in Fig. 7G, after ten days of treating the injuries, Giemsa staining was carried out to visualise micro organism within the tissue sections. In keeping with the bacterial counts from the tissue homogenates, ample micro organism have been noticed within the tissues of the management, HAZ MNs, and ZIF MNs teams.
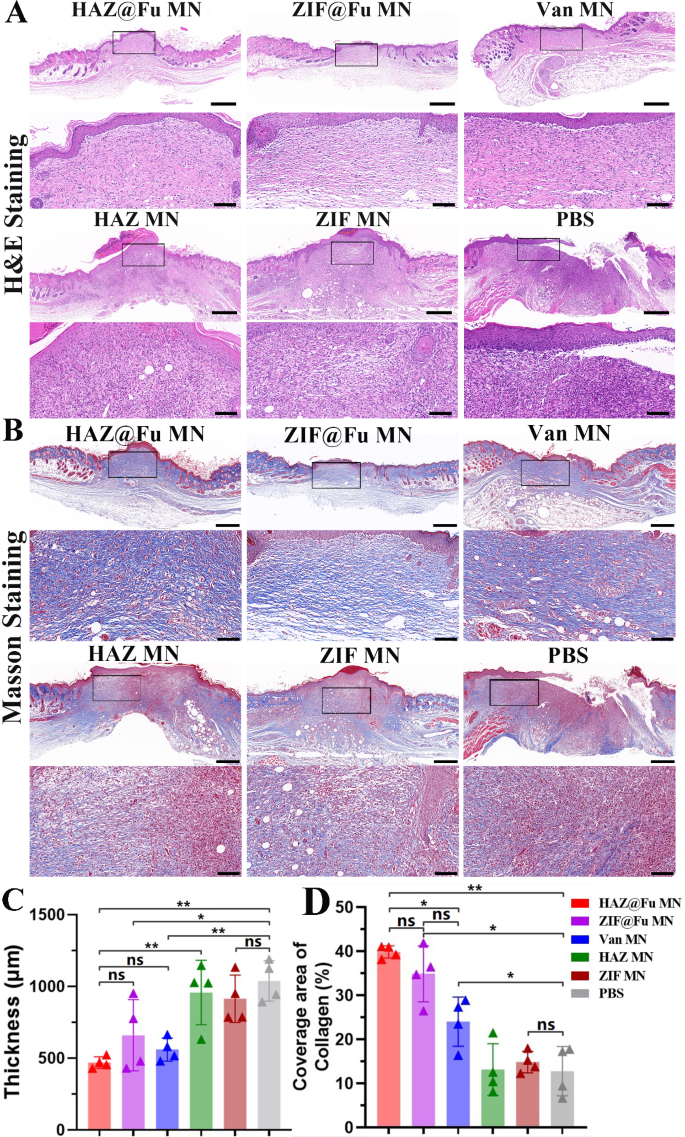
To look at the reconstruction of epidermal tissue, histological assessments have been carried out on Day 10. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was employed to analyze the regeneration of wound beds, the formation of granulation tissue, and the processes of epithelial formation. The thickness of the granulation tissue in every group have been additionally measured (Fig. S10). The Fig. 8A revealed {that a} new stratum corneum was absolutely fashioned within the HAZ@Fu MNs, ZIF@Fu MNs and Van MNs teams. The thickness of the granulation tissue was considerably diminished in comparison with that of ZIF MNs, HAZ MNs and management group. Furthermore, a substantial variety of inflammatory cells, which recognized by their excessive nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio and dominant nuclear staining, have been famous throughout the wound space and remaining scabs in ZIF MNs, HAZ MNs and management group.
Analysis of MRSA-infected wound therapeutic in Vivo. (A) Optical photos and the corresponding magnified photos of H&E staining (scale bar: 100 μm, 500 μm after magnification). (B) Optical photos and the corresponding magnified photos of Masson staining (scale bar: 100 μm, 500 μm after magnification). (C) Quantitative evaluation of granulation tissue thickness noticed within the H&E staining throughout six teams. (D) Quantitative evaluation of the protection space of collagen as noticed in Masson staining
Quantitative evaluation revealed a major discount within the thickness of granulation tissue with HAZ@Fu MNs remedy (440.60 ± 20.36 μm) compared to the management (997.80 ± 170.30 μm) and the ZIF MNs or HAZ MNs teams (Fig. 8C). It advised that HAZ@Fu MN group current improved regulation of irritation and accelerated tissue regeneration. Processes like collagen synthesis, deposition, and directional alignment, that are essential for tissue reworking, additionally play a major position in wound therapeutic, and masson staining was carried out to watch the collagen formation and deposition. Determine 8B confirmed a major space of newly fashioned collagen, characterised by its directional alignment and a deep blue stain, evident within the neotissue of the epithelium in each the ZIF@Fu and HAZ@Fu teams. Correspondingly, the extent of collagen protection was quantified as 39.87 ± 1.41% within the ZIF@Fu group and 35.18 ± 5.92% within the HAZ@Fu group, respectively. Which considerably increased than that within the Van MNs group (24.08 ± 5.59%, p < 0.05). These findings counsel an elevated quantity of collagen deposition and improved tissue reworking.
[ad_2]