
[ad_1]
A crew led by the Laboratory of Molecular Nanoscience of the School of Chemistry on the College of Barcelona has designed a brand new molecular compound based mostly on gadolinium (Gd), a chemical factor that may generate a magnetocaloric impact, that’s of explicit curiosity within the subject of molecular magnetism and within the design of gadgets with technological functions on the nanoscale.
The paper, printed within the Journal of Supplies Chemistry A, is authored by Professor Carolina Sañudo, from the UB’s School of Chemistry and the Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (IN2UB), and contains a lot of the analysis carried out by Subodh Kumar, a scholar of the UB’s grasp’s diploma in Nanosciences, and Ph.D. scholar Guillem Gabarró, each co-authors of the paper.
Magnetic refrigerants on the nanoscale
Two-dimensional (2D) supplies are compounds that present distinctive efficiency for designing heterostructures—the becoming a member of of various supplies with completely different properties—or for multifunctional gadgets. Particularly, the brand new compound relies on gadolinium (Gd), a uncommon earth chemical factor that has seven unpaired electrons and may act as a magnetic refrigerant.
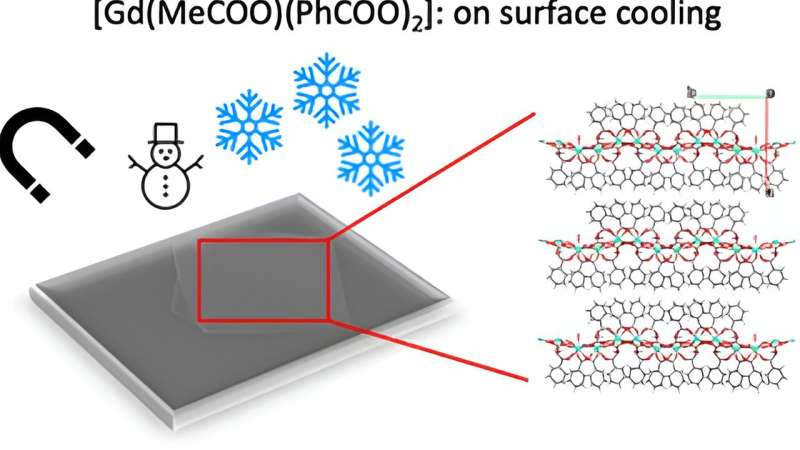
Within the examine, the crew of the UB’s Laboratory of Molecular Nanoscience has ready a 2D(III) composite. This compound is introduced within the form of a large lattice-type materials of steel cations and natural ligands (metal-organic framework, MOF). A particularity of Gd(III) compounds is that they’re energetic at extraordinarily low temperatures.
“This MOF is particular as a result of it’s two-dimensional. The 2D MOFs are metal-organic equivalents to graphene and, like this compound, might be exfoliated in monolayers or in aggregates of some monolayers on the nanometer scale,” says Carolina Sañudo, professor on the UB’s Division of Inorganic and Natural Chemistry.
On this compound, every Gd(III) ion behaves as if it have been a single molecule magnet (SMM). As it’s a 2D lattice compound, every monolayer is an ordered lattice of SMMs. As well as, it has a excessive magnetic entropy and a magnetocaloric impact (MCE) as a consequence of the truth that it comprises Gd(III).
“The examine of those multifunctional magnetic supplies includes a multidisciplinary activity the place the characterization of the supplies by numerous strategies, reminiscent of dc/ac magnetometry, calorimetry, luminescence and X-ray magnetic round dichroism, is essential,” notes Elena Bartolomé, researcher at ICMAB-CSIC.
Within the paper, the crew has succeeded in rising nanocrystals of the compound on a semiconducting silicon floor, a decisive step towards having the ability to use molecular supplies in gadgets for technological functions.
The findings of the brand new examine point out that it’s attainable to make use of gadolinium compounds for magnetic cooling in gadgets. “Not solely have we been capable of nanostructure the fabric on a semiconductor, however we now have proven that the magnetocaloric impact is maintained on the nanoscale, and the brand new compound can operate as a magnetic floor coolant,” says researcher Carolina Sañudo.
Two-dimensional lattice supplies—or 2D MOFs—have potential functions relying on the steel with which they’re shaped. The brand new composite has two key properties: it’s a magnet molecule (SMM) and displays the magnetocaloric impact (MCE). SMMs are magnet molecules that may be utilized as options to the miniaturization of data storage, the place every Gd(III) molecule or ion acts as a bit.
Having the SMMs completely ordered in 2D presents many benefits that the analysis group desires to use in future traces of analysis. Within the subject of magnetic refrigeration, the nanocrystals deposited on the semiconductor can be utilized as floor coolants at cryogenic temperatures, a property of curiosity to decrease the temperature inside digital circuits or gadgets.
Since 2020, the UB Molecular Nanoscience Laboratory has been working with compounds based mostly on uncommon earth components, reminiscent of dysprosium (Dy), terbium (Tb) and europium (Eu). “Dysprosium or terbium compounds are 2D lattice supplies of magnet molecules. With terbium, europium or mixtures of terbium and europium we are able to additionally get hold of extremely luminescent supplies that can be utilized as safety inks,” concludes Sañudo.
Extra data:
Subodh Kumar et al, On-surface magnetocaloric impact for a van der Waals Gd(iii) 2D MOF grown on Si, Journal of Supplies Chemistry A (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D3TA06648G
Supplied by
College of Barcelona
Quotation:
New molecular compound designed with technological functions on the nanoscale (2024, April 3)
retrieved 6 April 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-04-molecular-compound-technological-applications-nanoscale.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]