[ad_1]
Working in a theoretical group regularly entails having conversations in entrance of the information to make clear the narrative that nature is trying to convey. An intriguing discovery was made on the Madrid-based IMDEA Nanociencia Institute just lately.
Two layers of graphene stacked on prime of one another and barely stretched aside by a minute power are often called strained bilayer graphene. Dr. Pierre Pantaleón, a researcher on the Group of Theoretical Modelling at IMDEA Nanociencia, was speaking about this materials with Prof. Paco Guinea, the group chief when Paco noticed an irregularity that had missed the eye of everybody else; Pierre was demonstrating his animated depiction of strained graphene to the group.
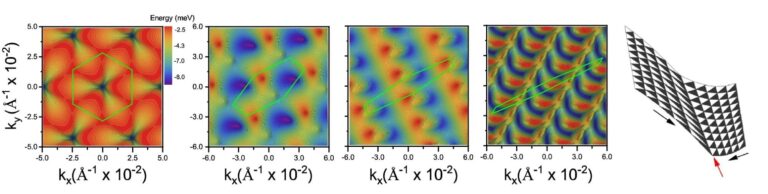
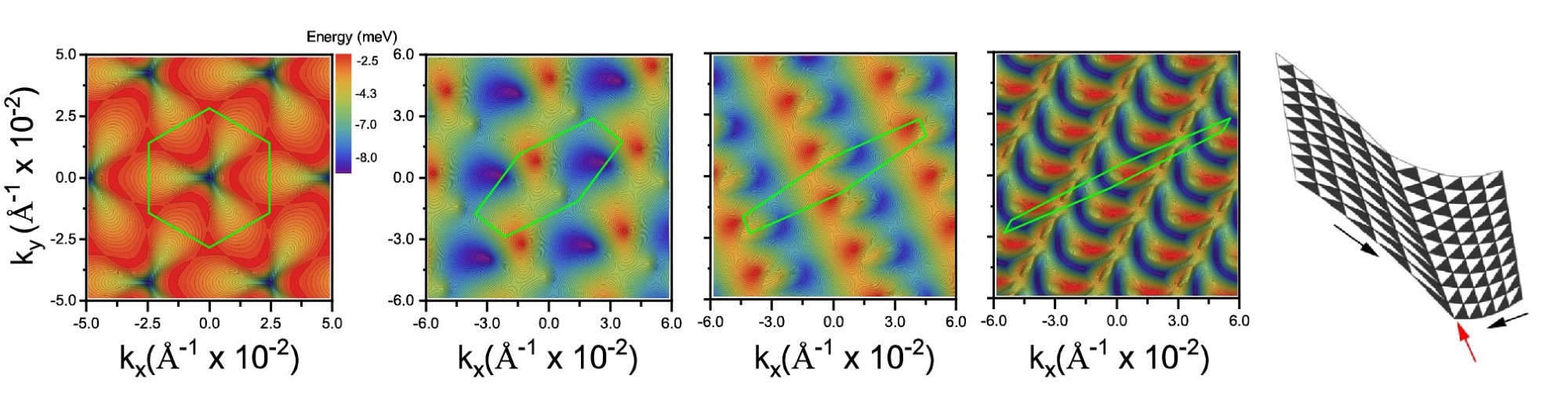
It seems that the Brillouin zone (the unit cell within the momentum area) of bilayer graphene is distorted and at last collapses in a single course when it’s underneath pressure. An inaccuracy in Pierre’s visualization program urged the existence of a singularity because of the distortion on the collapsing level.
Singularities, such because the one the researchers have been learning, name for critical consideration in physics. They could recommend that one thing is flawed, altering, or want extra investigation. At that time, Paco’s examine group included Dr. Andreas Sinner, a proficient theoretical physicist who was working at Opole College in Poland, and so they started investigating the singularity’s origin with Pierre.
What caught their curiosity was the simultaneous transformation in actual area: the 2-dimensional materials’s strained graphene led to the creation of practically flawless one-dimensional moiré patterns, or one-dimensional channels.
Via the usage of microscopes, scientists had beforehand noticed comparable occurrences and had written them off as design flaws like adhered supplies or dislocations. Take the work of McEuen (Cornell College), Mendoza (Rio de Janeiro College), or Zhu (Columbia College) as examples.
Nevertheless, the researchers now disclose masked impacts that have been hidden behind what gave the impression to be artifacts. It is a pure phenomenon that happens in hexagonal honeycomb lattices, similar to these present in graphene, in line with the examine staff at IMDEA Nanociencia. Particularly, pressure is given to 2 layers which can be positioned at a minor twist angle.
The researchers’ most vital discovering is the analytical options they discovered for the required pressure wanted to supply these one-dimensional channels. This resolution is surprisingly easy, relying solely on two variables: the twist angle and the Poisson ratio, a relentless distinctive to every materials.
Because of their analysis, they’ve developed a single mathematical components that describes the phenomenon and gives details about its bodily basis.
Though the physics they clarify of their examine, which was printed in Bodily Evaluation Letters, will not be novel, their elegant and one-of-a-kind rationalization of the phenomenon in such plain phrases—a single analytical expression—is. The outcomes pave the way in which for the engineering of recent supplies on surfaces with these kind of one-dimensional channels.
In contrast to their unrestricted mobility within the typical 2D graphene atmosphere, electrons are constrained inside these channels. These channels present a most popular course of movement for the electrons.
This discovering has far-reaching penalties, as its potential purposes will be expanded to different supplies, similar to dichalcogenides, and totally different geometric preparations.
The Group of Professor Guinea is presently engaged in a radical investigation into the potential of graphene in each twisted and non-twisted bilayers, encompassing the detection of superconductivity. An intensive evaluation was simply launched within the journal Nature Evaluations Physics.
This work is the results of the Theoretical Modelling Group at IMDEA Nanociencia, which has obtained funding from the Spanish Program on Superior Supplies, the NMAT2D and MAD2D regional grants, and the EU’s Graphene Flagship.
Journal Reference:
Sinner, A., et al. (2023) Pressure-Induced Quasi-1D Channels in Twisted Moiré Lattices. Bodily Evaluation Letters. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.166402
Pantaleón, P. A., et al. (2023) Superconductivity and correlated phases in non-twisted bilayer and trilayer graphene. Nature Evaluations Physics. doi:10.1038/s42254-023-00575-2
Supply: https://nanociencia.imdea.org/
[ad_2]