[ad_1]
By attaching molecules collectively, scientists at Université de Montréal assume they’ve discovered how molecular methods on the origin of life advanced to create complicated self-regulating capabilities.
Printed in Angewandte Chemie, their findings promise to offer chemists and nanotechnologists with a easy technique to create the following era of dynamic nanosystems.
Life on Earth is sustained by hundreds of thousands of various tiny nanostructures or nanomachines which have advanced over hundreds of thousands of years, defined Alexis Vallée-Bélisle, a UdeM professor and principal investigator of the examine.
These buildings, usually smaller than 10,000 instances the diameter of a human hair, are sometimes composed of proteins or nucleic acids. Whereas some are comprised of a single element or half (usually linear polymers that fold into a particular construction), most of them are made utilizing a number of elements that spontaneously assemble into massive and dynamic assemblies.
Responding to stimuli
“These molecular assemblies are extremely dynamic and activate or deactivate exactly in response to varied stimuli similar to a variation in temperature, oxygen, or vitamins,” stated Vallée-Bélisle.
“Equally to vehicles that require sequential ignition, brake launch, gear change and gasoline enter to maneuver ahead, molecular methods require the sequential activation or deactivation of varied nanomachines to carry out any particular duties starting from transferring, respiratory to considering.”
The researchers raised a elementary query: how have dynamic molecular assemblies been created, programmed and fine-tuned to assist life?
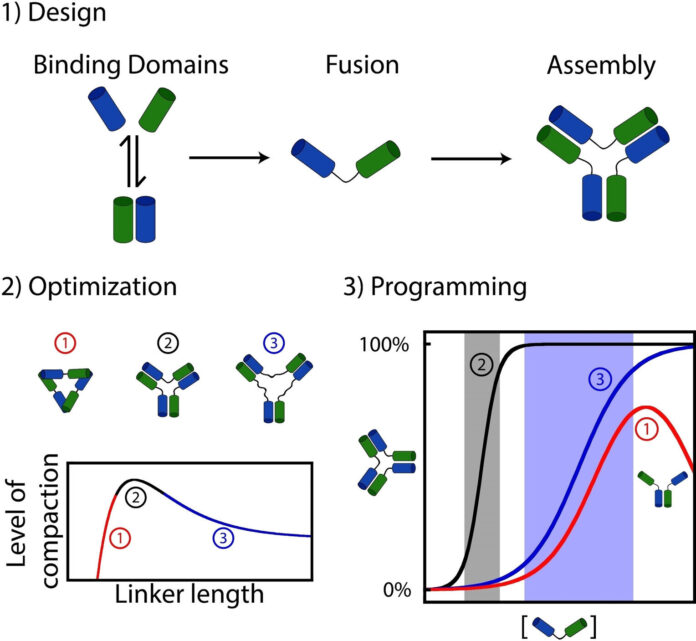
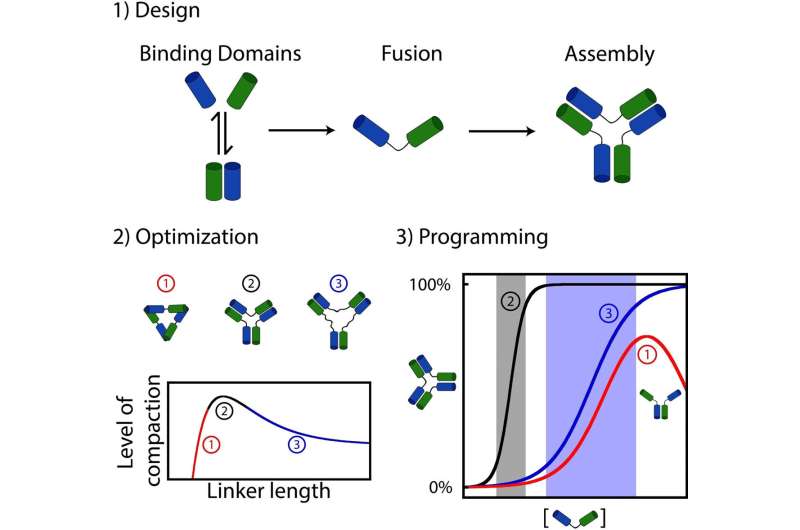
What they discovered is that many organic assemblies have been possible fashioned by randomly attaching interacting molecules (e.g., proteins or nucleic acids similar to DNA or RNA) with linkers performing like a “connector” between every half.
“As these biomolecular assemblies play a vital position in enabling residing organisms to reply to their atmosphere, we’ve hypothesized that the character of the connectivity between the connected elements may contribute to the evolution of their dynamic responses,” stated Vallée-Bélisle, holder of the Canada Analysis Chair in Bioengineering and Bio-Nanotechnology.
Exploring the affect of connectivity
To discover this query, Dominic Lauzon, a doctoral pupil on the time of the examine, determined to synthesize and fasten dozens of DNA interacting molecules collectively to discover the affect of connectivity on the dynamic of meeting.
“The programmable, easy-to-use, chemistry of nucleic acids similar to DNA makes it a handy molecule to check elementary questions associated to the evolution of biomolecules,” stated Lauzon, the primary writer of the examine. “Moreover, nucleic acids are additionally regarded as the molecule on the origin of life on Earth.”
Lauzon and Vallée-Bélisle found {that a} easy variation within the “linker” size between the interacting molecules results in important variations of their meeting dynamics. For example, sure assemblies exhibited excessive sensitivity to variation in stimuli, whereas others lacked such sensitivity, and even required a lot bigger adjustments in stimuli to advertise meeting.
Extra surprisingly, some linkers even created new complicated regulatory capabilities similar to self-inhibition properties, the place the addition of a stimulus would each promote its meeting and its disassembly. All these totally different responsive behaviors are additionally usually noticed in pure “residing” nanomachines.
Utilizing experiments and mathematical equations, the researchers have been additionally in a position to clarify why such a easy variation of linker size was so environment friendly at modifying the dynamics of molecular meeting.
“The linkers creating essentially the most steady assemblies have been those additionally creating essentially the most delicate activation mechanisms, whereas the linkers creating the much less steady assemblies created the much less delicate activation mechanisms, even to the purpose of introducing self-inhibition,” defined Lauzon.
Sensing is essential
The power to sense molecular indicators exactly is essential for organic assemblies but additionally within the growth of nanotechnology that will depend on the detection and integration of molecular info.
The researchers due to this fact imagine that their discovery may present the elemental framework to create extra programmable nanomachines or nanosystems with optimally regulated actions—as an illustration, by merely attaching interacting molecules with various linkers. Such molecular assemblies are already discovering purposes in biosensing or drug supply.
Along with offering a easy design technique to create the following era of self-regulated nanosystems, the scientists’ discoveries additionally make clear how pure biomolecular assemblies could have acquired their optimum dynamics.
“One well-known molecular evolution technique of residing organisms is gene fusion, the place the DNA coding for 2 interacting protein domains are randomly fused,” stated Vallée-Bélisle.
“Our findings additionally present the elemental understanding required to grasp how a easy variation within the linker size between the fused proteins could have effectively created organic assemblies displaying a wide range of dynamics, some higher suited than others to offer a bonus to residing organisms.”
Extra info:
Dominic Lauzon et al, Design and Thermodynamics Rules to Program the Cooperativity of Molecular Assemblies, Angewandte Chemie Worldwide Version (2023). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202313944
Offered by
College of Montreal
Quotation:
How molecular methods on the origin of life could have advanced: Rise of the nanomachines (2024, February 7)
retrieved 12 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-molecular-life-evolved-nanomachines.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]