[ad_1]
In a latest evaluation by HP, there’s a worrying development on the planet of cybercrime: simply accessible, pre-packaged malware kits are on the rise, permitting even these with restricted tech know-how to launch subtle assaults.
Right here’s what it’s best to know:
- Outdated Malware in New Packaging: A technique has emerged the place attackers are hiding previous malware, just like the decade-old Houdini VBScript RAT, inside seemingly innocuous information, akin to transport paperwork. It’s a stark reminder that even previous threats can return in new guises.
- Misleading Double-Dealing Assaults: Some attackers are utilizing a tactic the place two actions kick off from a single malicious doc. One shows a legitimate-looking bill, distracting the person, whereas the opposite quietly runs dangerous malware within the background. Notably, the instruments for such assaults can be found for as little as $65 a month on hacking boards.
Alex Holland from HP, a senior malware analyst, remarked on the benefit with which these assaults will be executed. “With the rise of ‘DIY malware kits’, attackers don’t must be tech wizards. They simply purchase these kits, which might exploit legit instruments, making detection even tougher.”
Curiously, the report additionally highlighted a sneaky trick the place some cybercriminals are deceptive newbies. Faux malware-building kits are being offered on platforms like GitHub, tricking inexperienced hackers into by accident infecting their very own units.
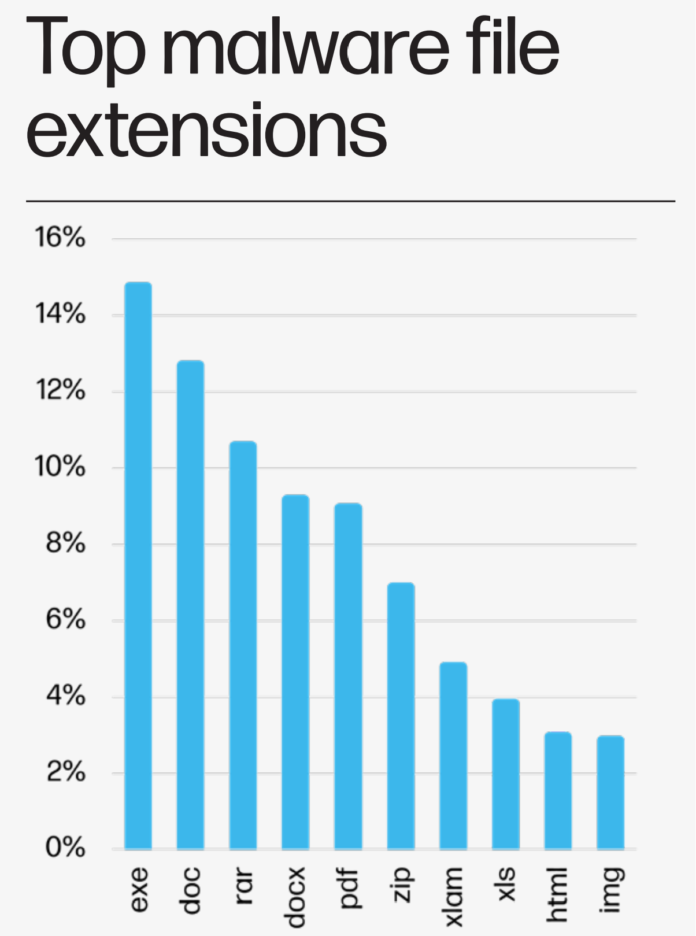
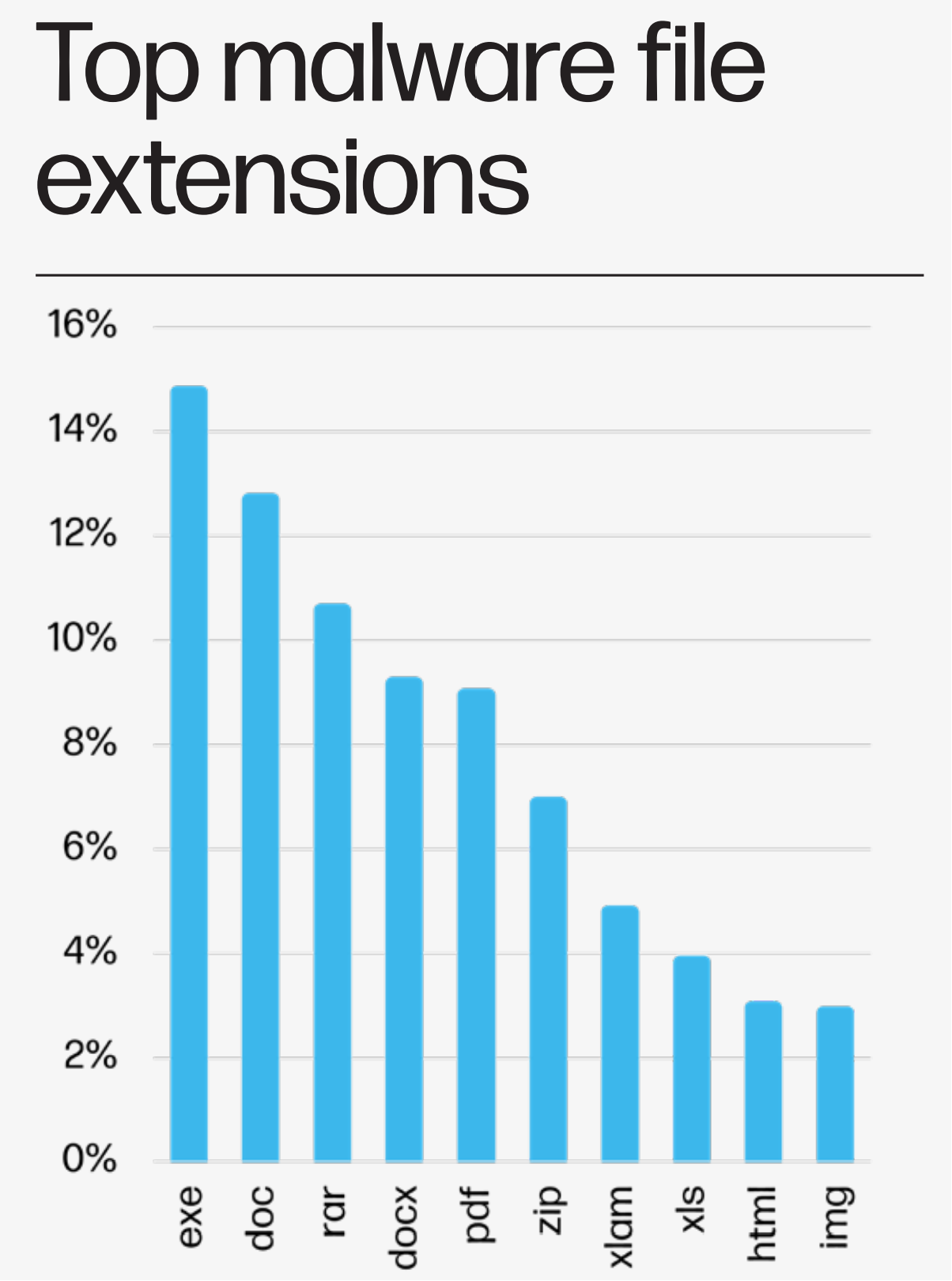
High Malware File Extensions
The HP Wolf Safety Menace Insights Report for Q3 2023 emphasizes the various vary of file extensions being exploited by malware builders. Most notably, executable information (.exe) stay a major alternative for malware distribution. Conventional doc codecs like .doc, .docx, and .pdf proceed to be exploited, underscoring the significance of treating even acquainted file varieties with warning. The prominence of compressed codecs like .rar and .zip highlights the necessity for rigorous safety protocols when unpacking archives. As cyber threats evolve, understanding and consciousness of such malware vectors stay essential for proactive protection.
Another essential findings from HP’s evaluation:
- Archives as Malware Carriers: For the sixth time in a row, archives stay the favourite technique for malware supply.
- Rise in File Extension Misuse: There’s been an alarming rise within the misuse of macro-enabled Excel add-ins and PowerPoint add-ins for malware distribution.
- Uncaught Threats: A stunning 12% of electronic mail threats slip by electronic mail gateway scanners, as recognized by HP’s Positive Click on device.
- Elevated Exploits in Frequent Instruments: Q3 noticed a big rise in malware exploiting each Excel (91%) and Phrase (68%).
- PDFs as Threats: Malware contained in PDFs elevated by 5% in Q3.
- Major Assault Sources: Most cyberattacks in Q3 got here through electronic mail (80%), with browser downloads being the second commonest supply (11%).
Holland suggests a defensive technique: “Given how accessible these malware kits have develop into, companies ought to deal with isolating duties which can be extra susceptible, like viewing electronic mail attachments or clicking on hyperlinks. It’s all about decreasing the alternatives for malware to get in.”
In essence, HP’s evaluation underscores the necessity for fixed vigilance and adaptation in cybersecurity methods. With instruments like HP’s Wolf Safety, dangerous duties are remoted in digital environments, serving to to reduce threats and offering insights into evolving cybercrime ways.
By Randy Ferguson
[ad_2]